Health
Long-range and short-range risk of airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2
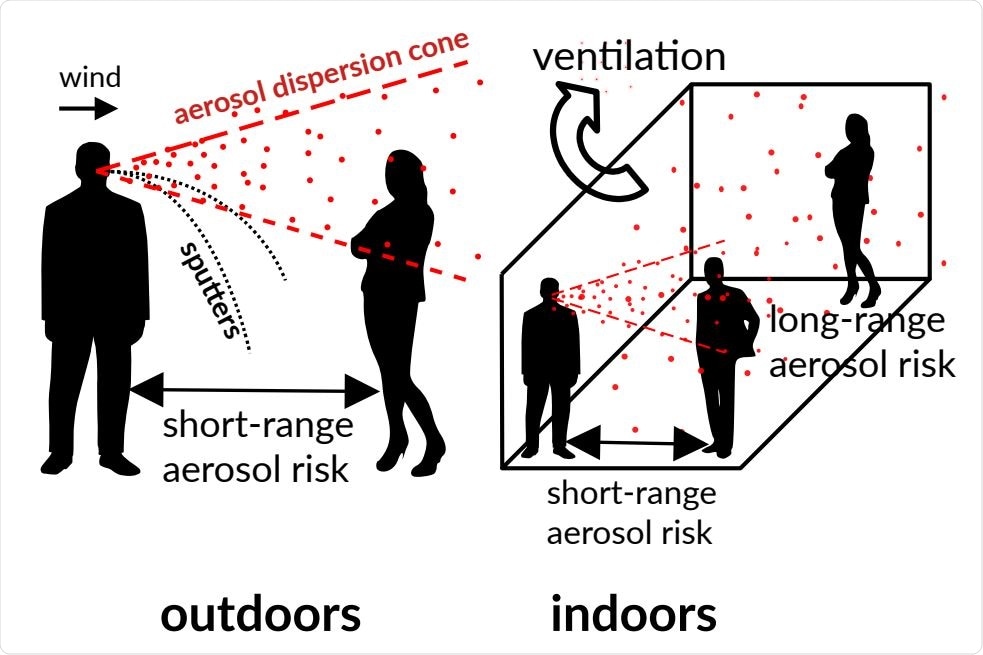
The pandemic of COVID-19 caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) contributes to significant morbidity, mortality, and financial loss. To date, the virus has infected more than 159 million people and killed more than 3.3 million people worldwide. The need to mitigate this pandemic has led the scientific community to reassess its infectivity, mechanism, and risk of infection under certain conditions.
Recent research shows Florian Poydenot et al. We conducted a quantitative assessment of the risk of infection indoors and outdoors. And how to reduce the contribution of public space to the propagation of SARS-CoV-2.The study is published in medRxiv*, Health science preprint server.
“Quantitative analysis of the risk of viral infection in public places can identify the key mechanisms by which preventative public health policies can act to mitigate risk and assess the resulting risk mitigation.”
Researchers have shown that long-range aerosol propagation is controlled by fresh air flow and mask filtration quality and is quantitatively associated with CO2 concentration, regardless of room volume or number of people. .. Importantly, they found that it was quantitatively related to CO2 concentration, regardless of room volume or number of people.

SARS-CoV-2 long-range and short-range aerial propagation
Researchers have ly investigated short-range aerial transmission using dedicated distributed experiments conducted at two shopping malls. They found that the exhaled aerosol was dispersed by a conical turbulent draft, leading to a concentration that was inversely proportional to the square of the distance and the flow velocity.
They elaborated on the various technologies available to reduce the risk of viral infections in public places. In this study, researchers showed that an average infection level, called a viral quantum, could be determined from epidemiological data (in a manner consistent with biological data).
In this study, researchers defined and modeled transmission risk, focusing on indoor and outdoor long-range aerial transmission risk (measured using carbon dioxide concentration) and short-range aerial transmission risk. .. They investigated the quantum generation rate and dose-response function.

(A) Without mask (b) With surgical mask (c) Schlieren imaging of a person with FFP2 mask. Temperature acts as a passive scalar for turbulent transport, similar to CO2 and small aerosols. Schlieren technology shows a local change in the index of refraction of air caused by warm air expelled from the body.
They also investigated the efficiency of respiratory masks based on droplet size distribution, droplet evaporation (controlled by ambient relative humidity RH), and concentration issues.
SARS-CoV-2 can easily spread during exhaled human activity (breathing, talking, singing, laughing, etc.) and can cause asymptomatic and presymptomatic infections (as aerosols). It has been established. It has also been observed that indoor infections are 19 times more common than outdoors.
Measuring the risk of virus infection in public places (schools, offices, university auditoriums, museums, theaters, shopping centers, etc.) and outdoors is a problem. Researchers in this study have sought to characterize major transmission routes in social activities and identify efficient ways to reduce the risk of epidemic contamination in public spaces.
In this comprehensive study, researchers define the risk of infection in public places to the number of people present, the average time they are present, the amount of aerosol stored, and the level of ventilation. Document the dependencies of.
They determined a risk assessment for long-range aerial transmission and associated it quantitatively with CO2 levels.
Interestingly, this study showed that localized short-range aerial transmission after people infected with SARS-CoV-2 follows the same physics indoors and outdoors.
Experimental measurements of turbulent dispersion of passive tracers (CO2) performed in shopping centers have shown that turbulent diffusion is due to small permanent airflows leading to rapid spatial decay of tracer concentrations. They report that the additional risk of waking up from others is quantitatively determined as a function of leeward distance.
In conclusion, researchers provide a practical definition of risk r (Defined as the average secondary infection per person who was first infected) Related to public spaces. This is related to the integrated quantum emission, mask filtration factor (λ), and CO2 concentration that quantifies the dilution factor between exhaled air and inspiratory air.
Based on this risk assessment, researchers have defined quantitative criteria (occupancy, CO2 levels, ventilation, masks) to be implemented in public spaces to reach acceptable residual risk.
The goal of efforts to mitigate COVID-19 is to reduce the pandemic to a level where the overall virus regeneration rate is less than one. This study prevents major routes of viral infection through enhanced ventilation, air purification, and mechanical dispersion using fans, and may be covered with properly fitted high quality facial masks (surgical masks). There is another fabric mask, or by a non-medical FFP2 mask).
Combining these measures will significantly reduce the risk of SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the air.
*Important Notices
medRxiv Publish preliminary scientific reports that should not be considered definitive as they are not peer-reviewed, guide clinical practice / health-related behaviors, and should not be treated as established information.
Journal reference:
- Risk assessment of long- and short-range aerial transmission of SARS-CoV-2 indoors and outdoors using carbon dioxide measurements, Florian Poydenot, Ismael Abdourahamane, Elsa Caplain, Samuel Der, Jacques Haiech, Antoine Jallon, Inés Khautami, Amir Loucif, Emil Marinov, Bruno Andreotti, medRxiv 2021.05.04.21256352; Doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.04.21256352, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.05.04.21256352v1
..
What Are The Main Benefits Of Comparing Car Insurance Quotes Online
LOS ANGELES, CA / ACCESSWIRE / June 24, 2020, / Compare-autoinsurance.Org has launched a new blog post that presents the main benefits of comparing multiple car insurance quotes. For more info and free online quotes, please visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/the-advantages-of-comparing-prices-with-car-insurance-quotes-online/ The modern society has numerous technological advantages. One important advantage is the speed at which information is sent and received. With the help of the internet, the shopping habits of many persons have drastically changed. The car insurance industry hasn't remained untouched by these changes. On the internet, drivers can compare insurance prices and find out which sellers have the best offers. View photos The advantages of comparing online car insurance quotes are the following: Online quotes can be obtained from anywhere and at any time. Unlike physical insurance agencies, websites don't have a specific schedule and they are available at any time. Drivers that have busy working schedules, can compare quotes from anywhere and at any time, even at midnight. Multiple choices. Almost all insurance providers, no matter if they are well-known brands or just local insurers, have an online presence. Online quotes will allow policyholders the chance to discover multiple insurance companies and check their prices. Drivers are no longer required to get quotes from just a few known insurance companies. Also, local and regional insurers can provide lower insurance rates for the same services. Accurate insurance estimates. Online quotes can only be accurate if the customers provide accurate and real info about their car models and driving history. Lying about past driving incidents can make the price estimates to be lower, but when dealing with an insurance company lying to them is useless. Usually, insurance companies will do research about a potential customer before granting him coverage. Online quotes can be sorted easily. Although drivers are recommended to not choose a policy just based on its price, drivers can easily sort quotes by insurance price. Using brokerage websites will allow drivers to get quotes from multiple insurers, thus making the comparison faster and easier. For additional info, money-saving tips, and free car insurance quotes, visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ Compare-autoinsurance.Org is an online provider of life, home, health, and auto insurance quotes. This website is unique because it does not simply stick to one kind of insurance provider, but brings the clients the best deals from many different online insurance carriers. In this way, clients have access to offers from multiple carriers all in one place: this website. On this site, customers have access to quotes for insurance plans from various agencies, such as local or nationwide agencies, brand names insurance companies, etc. "Online quotes can easily help drivers obtain better car insurance deals. All they have to do is to complete an online form with accurate and real info, then compare prices", said Russell Rabichev, Marketing Director of Internet Marketing Company. CONTACT: Company Name: Internet Marketing CompanyPerson for contact Name: Gurgu CPhone Number: (818) 359-3898Email: [email protected]: https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ SOURCE: Compare-autoinsurance.Org View source version on accesswire.Com:https://www.Accesswire.Com/595055/What-Are-The-Main-Benefits-Of-Comparing-Car-Insurance-Quotes-Online View photos
Pictures Credit
to request, modification Contact us at Here or [email protected]



