Uncategorized
Watch the volcano: a continuous eruption of Kilauea: a lava lake
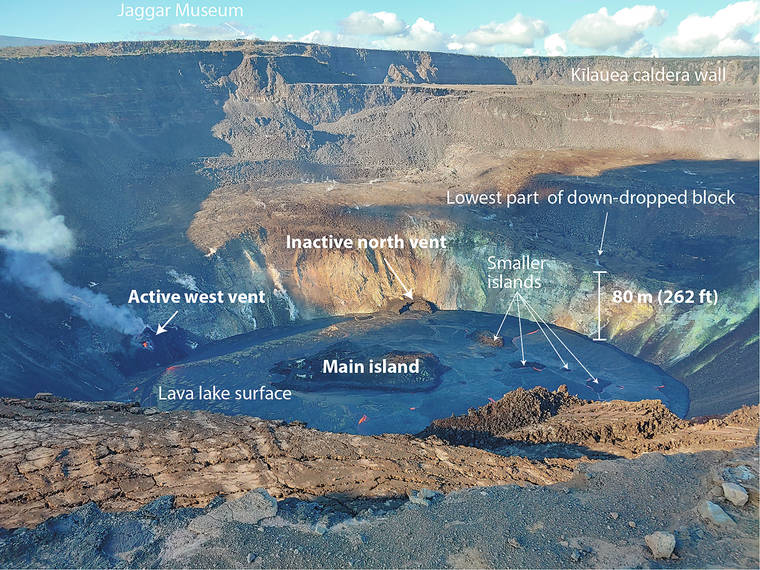
It was an exciting week at Kilauea volcano as the eruption of the summit that began on the evening of December 20 continued. The eruption remains confined within the papilla crater. The monitoring data shows no signs of activity shifting from the summit to the rift zones, nor any indications of the summit collapse like the one that occurred in 2018.
The primary danger from this eruption at this time is vog (volcanic air pollution) caused by gases emitted at the summit. USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory scientists continue to closely monitor the eruption.
As “Volcano Watch” was published last week, lava continued to erupt from two vents on the western and northern sides of the Halema’uma’u crater at a total rate of about 30 cubic meters (1,060 cubic feet) per second. The height of the lava lake was slowing due to the funnel-like shape of Halema’uma’u.
By Christmas Eve, the lava lake rose slightly above the level of the northern aperture, which had until now been the dominant source of lava for the eruption. Lava fountains from the northern aperture, which built an amphitheater-shaped cone surrounding it, pushed the circulation of the lava lake visible in the movement of the crust.
Early in the morning on December 26th, the largest change in volcanic activity was observed. At around 3 AM HST, activity in the western hole increased dramatically as the fountain in the northern hatch diminished. HVO scientists observing the lake saw lava drain back into the northern opening and the lake level dropped 5 meters (26 feet) over the next few hours. This left a “bathtub loop” around the edge of the lake, indicating the lake’s highest point. The change in active venting also saw a decrease in sulfur dioxide (SO2) production, from 16,000 to 20,000 tons per day on December 25 to 3,800 tons per day on December 30.
The level of the lava lake has slowly risen again since December 27, and as of writing this article, it has reached a new height of 701 meters (2,300 feet) above sea level (highest) and 184 meters (603 feet) deep. The size of the blisters up to this point is more than 20 million cubic meters (700 million cubic feet) or about 8,000 Olympic-sized swimming pools! The eruption rate has decreased to about 10 cubic meters (353 cubic feet) per second. On December 30, the lake was 800 m (875 yd) from east to west and 530 m (580 yd) from north to south, and covered an area of 33 hectares (82 acres). Lava continues to erupt from the western opening.
One of the most common questions asked by HVO is, “When will the lake be visible from an open area in Hawai’i Volcanoes National Park?” And does a lava lake fill Halima? These questions are difficult to answer because the activity within the papilla is dynamic. After the eruption first began, the lava lake rose rapidly due to the base shape of Halema’uma’u (inverted cone) and the initially high rates of lava eruption.
Since then, the rate of lava eruption has varied, particularly as activity moves from the northern orifice to the west, with the accompanying lava depletion into the inactive northern opening and a temporary decrease in lake level. However, HVO has done some initial calculations to try to answer these questions using topographic models and the most recent eruption rate.
The lava lake should be visible from the Kilauea Overlook once it reaches a height of just over 780 meters (2,560 feet) above sea level, then 5 meters (16 feet) of elevation will make it overflow to the lower edge of Halema’uma’u at Northeast side. Since the lava lake is currently about 701 meters (2,300 feet) above sea level, it has about 80 meters (262 feet) in elevation before it reaches visibility. When it does that depends on the rate of lava eruption.
Assuming a constant eruption rate of 10 cubic meters (353 cubic feet) per second, it would take approximately forty-five days to fill the lava to just over 780 meters (2,560 feet) above sea level, and thus become visible from Kilauea overlooking . After several days, it will begin to flow over the lower rim of Halema’uma’u at just under 800 meters (2,625 feet) above sea level. However, it will likely take longer due to the fluctuation of the eruption rate and its overall decrease. If the lava exceeds Halema’uma’u, it will then need to fill in the extensive flocculent mass area before it overflows onto the floor of the main caldera.
HVO continues to closely monitor this eruption at Halema’uma’u at the summit of Kilauea. Check the HVO website for image, video and text updates: www.usgs.gov/hvo.
Volcano activity updates
Kilauea volcano erupting. The USGS Volcano Alert Level is at WATCH (https://www.usgs.gov/natural-hazards/volcano-hazards/about-alert-levels). Kilauea updates are released daily.
Activity is limited to Halema’uma’u with lava erupting from vents on the northwest side of the crater. Over the past 24 hours, measurements of the depth of the lava lake have ranged from 181 meters to 185 meters (593 to 608 feet). A preliminary analysis of the sulfur dioxide emission rates measured on Wednesday (30 December) shows the rates to be around 3,800 tons / day, in the range of common values for the lava lake before 2018. The summit tilt measures have not recorded any inflationary or deflationary tendencies over the past two days. The earthquakes remained high but stable, with continuous high tremor and few minor earthquakes. For the most recent information on the eruption, see https://www.usgs.gov/volcanoes/Kilauea/current-eruption.
Mauna Loa does not erupt and remains at Volcano Alert Level.
This alert level does not imply that an outbreak is imminent or that progression to an outbreak from the current level of disturbance is certain. Mauna Loa updates are released weekly.
Last week, about 60 small-scale earthquakes were recorded under the upper elevations of Mauna Loa; Most of these occurred at depths of less than 8 kilometers (about 5 miles). The largest earthquake ever recorded was M2.2 below the volcano’s northwest flank on December 28 at 12:47 AM GMT. Earthquake activity on the northwestern side of Mauna Loa, which began on December 4, 2020, has decreased to average long-term trends. GPS measurements have recorded a contraction across the caldera summit since mid-October with resumption of the extension (peak swelling) in the past few weeks, consistent with the supply of magma to the shallow storage system of the volcano. Gas concentrations and fumarole temperatures at both the summit and the sulfur cone in the southwest rift region remain stable. The webcam shows have not revealed any changes to the scene over the past week. For more information on the current monitoring of Mauna Loa volcano, see: https://volcanoes.usgs.gov/volcanoes/mauna_loa/monitoring_summary.html.
There were 7 events with 3 or more hairy reports in the Hawaiian Islands during the past week: the M2.8 2 km (1 mi) earthquake east of Pahala at a depth of 33 km (20 mi) on December 28 at 1:26 PM HST, the M2 earthquake. 8 9 km (5 mi) ENE from Pahala at a depth of 31 km (19 mi) occurred on December 26 at 5:55 AM HST, M2.2 earthquake 6 km (3 mi) ENE from Pahala at a depth of 30 km (19 mi) Mi) occurred on December 24 at 7:56 pm GMT, an M1.7 earthquake occurred 6 km (3 mi) ENE from Pahala at a depth of 32 km (20 mi) on December 24 at 7:28 pm HST, occurred M3.6 7 km (4 mi) ENE earthquake from Pahala at a depth of 33 km (20 mi) on December 24 at 7:18 pm HST, M3.3 earthquake 8 km (4 mi) northeast from Pahala at a depth of 32 km ( 19 mi) occurred on Dec. 24 at 7:13 p.m. HST, and a M1.7 2 km (1 mi) earthquake occurred south of Pahala at a depth of 33 km (20 mi) on Dec.24 at 7:12 p.m. HST.
HVO continues to closely monitor both the ongoing Kilauea and Mauna Loa eruptions for any signs of increased activity.
Please visit the HVO website for previous Volcano Watch articles, Kilauea and Mauna Loa updates, volcano photos, maps, recent earthquake information, and more. Questions emailed to [email protected].
What Are The Main Benefits Of Comparing Car Insurance Quotes Online
LOS ANGELES, CA / ACCESSWIRE / June 24, 2020, / Compare-autoinsurance.Org has launched a new blog post that presents the main benefits of comparing multiple car insurance quotes. For more info and free online quotes, please visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/the-advantages-of-comparing-prices-with-car-insurance-quotes-online/ The modern society has numerous technological advantages. One important advantage is the speed at which information is sent and received. With the help of the internet, the shopping habits of many persons have drastically changed. The car insurance industry hasn't remained untouched by these changes. On the internet, drivers can compare insurance prices and find out which sellers have the best offers. View photos The advantages of comparing online car insurance quotes are the following: Online quotes can be obtained from anywhere and at any time. Unlike physical insurance agencies, websites don't have a specific schedule and they are available at any time. Drivers that have busy working schedules, can compare quotes from anywhere and at any time, even at midnight. Multiple choices. Almost all insurance providers, no matter if they are well-known brands or just local insurers, have an online presence. Online quotes will allow policyholders the chance to discover multiple insurance companies and check their prices. Drivers are no longer required to get quotes from just a few known insurance companies. Also, local and regional insurers can provide lower insurance rates for the same services. Accurate insurance estimates. Online quotes can only be accurate if the customers provide accurate and real info about their car models and driving history. Lying about past driving incidents can make the price estimates to be lower, but when dealing with an insurance company lying to them is useless. Usually, insurance companies will do research about a potential customer before granting him coverage. Online quotes can be sorted easily. Although drivers are recommended to not choose a policy just based on its price, drivers can easily sort quotes by insurance price. Using brokerage websites will allow drivers to get quotes from multiple insurers, thus making the comparison faster and easier. For additional info, money-saving tips, and free car insurance quotes, visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ Compare-autoinsurance.Org is an online provider of life, home, health, and auto insurance quotes. This website is unique because it does not simply stick to one kind of insurance provider, but brings the clients the best deals from many different online insurance carriers. In this way, clients have access to offers from multiple carriers all in one place: this website. On this site, customers have access to quotes for insurance plans from various agencies, such as local or nationwide agencies, brand names insurance companies, etc. "Online quotes can easily help drivers obtain better car insurance deals. All they have to do is to complete an online form with accurate and real info, then compare prices", said Russell Rabichev, Marketing Director of Internet Marketing Company. CONTACT: Company Name: Internet Marketing CompanyPerson for contact Name: Gurgu CPhone Number: (818) 359-3898Email: [email protected]: https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ SOURCE: Compare-autoinsurance.Org View source version on accesswire.Com:https://www.Accesswire.Com/595055/What-Are-The-Main-Benefits-Of-Comparing-Car-Insurance-Quotes-Online View photos
Picture Credit!
to request, modification Contact us at Here or [email protected]



