Health
Unraveling the role of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in lung injury: revealing a promising new approach
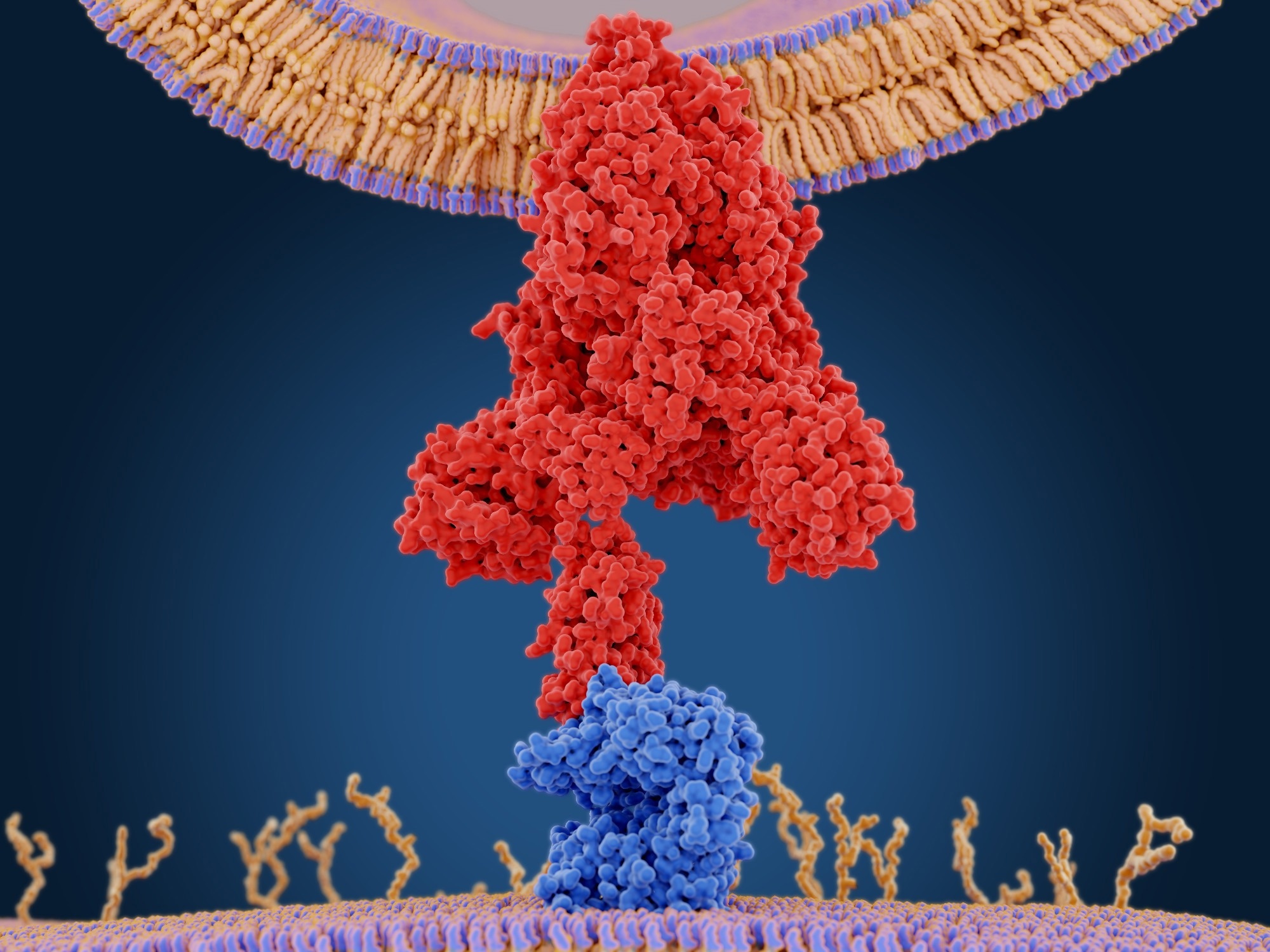
In a recent study published in scientific reportresearchers investigated the effects of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike (S) protein subunit 1 (S1) on lung endothelium.
 study: The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces lung endothelial cell dysfunction and thrombo-inflammation in response to C3a/C3a receptor signaling. Image credit: JuanGaertner/Shutterstock.com
study: The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces lung endothelial cell dysfunction and thrombo-inflammation in response to C3a/C3a receptor signaling. Image credit: JuanGaertner/Shutterstock.com
Background
The 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has caused unprecedented morbidity and mortality worldwide. Studies have reported that the SARS-CoV-2 S1 protein interacts with endothelial cells.
However, data on the detrimental effects of this protein on pulmonary vasculature and the mechanisms underlying SARS-CoV-2 infection are limited.
About research
Currently live In the study, researchers evaluated SARS-CoV-2 S1-induced endothelial cell damage in the pathogenesis of novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
To enhance SARS-CoV-2 S1 binding activity, the researchers utilized transgenic mouse animals in which the endogenous mouse angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) protein sequence was replaced with human ACE2-complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA). Mice were intravenously administered 35.0 grams (g) of SARS-CoV-2 S1 protein and sacrificed after 3 and 7 days.
To study the detrimental function of complement activation in the development of pulmonary vascular injury in hACE2-expressing mice infused with S1, we assessed C3 deposition in lung tissue. The total number of C3-positive von Willebrand factor (vWF)-labeled pulmonary arteries was assessed to determine the amount of C3 deposits within the pulmonary vasculature.
The researchers further examined the expression of cluster 46 of differentiation (CD46), an external complement regulator, and reported that it suppresses the production of C3 convertase through the alternative, conventional, and lectin pathways.
They also investigated the potential activity of the C3a/C3a receptor (C3aR) axis in SARS-CoV-2 S1-induced lung tissue injury by examining specific C3aR levels at different time points across several lung compartments.
To determine whether S1 infusion caused pulmonary vascular cell damage in hACE2-expressing mice, the research team quantified a number of biomarkers associated with thromboinflammatory processes, such as thrombomodulin (TM). Using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), he examined the lung tissue of his hACE2-expressing animals one week after S1 injection.
The researchers evaluated the effects of daily injections of the C3a receptor antagonist (C3aRa) SB290157 beginning 8 h after SARS-CoV-2 S1 infusion in hACE2-expressing animals, and established that complement activation was critical for enhancing S1-induced endothelial damage in lung tissue.
They also investigated the effect of C3aRa on inflammatory cell infiltration in the lungs of S1-treated mouse animals. Immunofluorescence analysis was performed to assess specific her MAC2 and GR1 levels to quantify macrophages and neutrophils, respectively.
result
In mice transgenic for human ACE2, S1 injection induced early loss of pulmonary endothelial thrombosis resistance at 3 days, resulting in loss of thrombomodulin and increased vWF levels.
S1 exocytosis and endothelial activation persisted, and fibrin (ogen) deposition co-stained with CD41-positive platelets within vessels was significantly increased in response to SARS-CoV-2 S1. C3aRa treatment inhibited C3a/C3aR activation and pulmonary C3 deposition, and attenuated vascular thrombus inflammation and fibrosis.
Histopathological evaluation of lung tissue on day 7 showed diffuse alveolar damage, thickening of alveolar septa, and hypercellularity in lung tissue.
A significant reduction in CD46 protein expression was observed in alveolar epithelial and endothelial cells. TEM analysis showed endothelial swelling in specific areas of the pulmonary circulation and arterioles.
SB290157 treatment significantly reduced SARS-CoV-2 S1-induced endothelial C3 deposition and restored CD46 on day 7. C3aRa treatment restored her TM expression and reduced von Willebrand factor staining in the vessel wall within 7 days.
Prominent deposition of GR1-positive neutrophils and MAC2-positive macrophages was observed in lung tissue 1 week after SARS-CoV-2 S1 infusion, indicating that early complement activation is critical for the recruitment of inflammatory cells to lung tissue. C3aRa treatment was effective in preventing SARS-CoV-2 S1-induced NET formation.
C3aRa treatment preserved alveolar architecture in hACE2-expressing mouse animals injected with SARS-CoV-2 S1 at 7 days and reduced alveolar morphological damage and lung parenchymal fibrosis.
The observation that C3aR antagonists block endothelial C3 deposition can be explained by previous studies showing that C3a promotes exocytosis of Weibel-Palade bodies, resulting in recruitment of the vascular surface to release prothrombotic P-selectin, tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), and vWF.
Conclusion
The study results showed that SARS-CoV-2 S1 stimulated vascular dysfunction and complement activation critical to pulmonary thromboinflammatory injury. Lung injury is characterized by early endothelial dysfunction leading to thromboinflammatory and fibrotic damage.
Lung injury was prominent at 3 days post-injection and was characterized by loss of TM and increase in vascular vWF.
Early complement activation coincided with endothelial dysfunction with deposition of C3 and elevated C3aR expression in both epithelial and endothelial cells.
The results of this study suggest that C3a and C3aR are potential therapeutic targets in patients with COVID-19, and that early treatment with complement inhibitors is preferable in severe cases.
|
Sources 2/ https://www.news-medical.net/news/20230719/SARS-CoV-2-spike-proteins-role-in-lung-injury-unraveled-promising-new-approach-uncovered.aspx The mention sources can contact us to remove/changing this article |
What Are The Main Benefits Of Comparing Car Insurance Quotes Online
LOS ANGELES, CA / ACCESSWIRE / June 24, 2020, / Compare-autoinsurance.Org has launched a new blog post that presents the main benefits of comparing multiple car insurance quotes. For more info and free online quotes, please visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/the-advantages-of-comparing-prices-with-car-insurance-quotes-online/ The modern society has numerous technological advantages. One important advantage is the speed at which information is sent and received. With the help of the internet, the shopping habits of many persons have drastically changed. The car insurance industry hasn't remained untouched by these changes. On the internet, drivers can compare insurance prices and find out which sellers have the best offers. View photos The advantages of comparing online car insurance quotes are the following: Online quotes can be obtained from anywhere and at any time. Unlike physical insurance agencies, websites don't have a specific schedule and they are available at any time. Drivers that have busy working schedules, can compare quotes from anywhere and at any time, even at midnight. Multiple choices. Almost all insurance providers, no matter if they are well-known brands or just local insurers, have an online presence. Online quotes will allow policyholders the chance to discover multiple insurance companies and check their prices. Drivers are no longer required to get quotes from just a few known insurance companies. Also, local and regional insurers can provide lower insurance rates for the same services. Accurate insurance estimates. Online quotes can only be accurate if the customers provide accurate and real info about their car models and driving history. Lying about past driving incidents can make the price estimates to be lower, but when dealing with an insurance company lying to them is useless. Usually, insurance companies will do research about a potential customer before granting him coverage. Online quotes can be sorted easily. Although drivers are recommended to not choose a policy just based on its price, drivers can easily sort quotes by insurance price. Using brokerage websites will allow drivers to get quotes from multiple insurers, thus making the comparison faster and easier. For additional info, money-saving tips, and free car insurance quotes, visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ Compare-autoinsurance.Org is an online provider of life, home, health, and auto insurance quotes. This website is unique because it does not simply stick to one kind of insurance provider, but brings the clients the best deals from many different online insurance carriers. In this way, clients have access to offers from multiple carriers all in one place: this website. On this site, customers have access to quotes for insurance plans from various agencies, such as local or nationwide agencies, brand names insurance companies, etc. "Online quotes can easily help drivers obtain better car insurance deals. All they have to do is to complete an online form with accurate and real info, then compare prices", said Russell Rabichev, Marketing Director of Internet Marketing Company. CONTACT: Company Name: Internet Marketing CompanyPerson for contact Name: Gurgu CPhone Number: (818) 359-3898Email: [email protected]: https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ SOURCE: Compare-autoinsurance.Org View source version on accesswire.Com:https://www.Accesswire.Com/595055/What-Are-The-Main-Benefits-Of-Comparing-Car-Insurance-Quotes-Online View photos
to request, modification Contact us at Here or [email protected]



