Health
Confirmation: Women accumulate entanglement faster than men
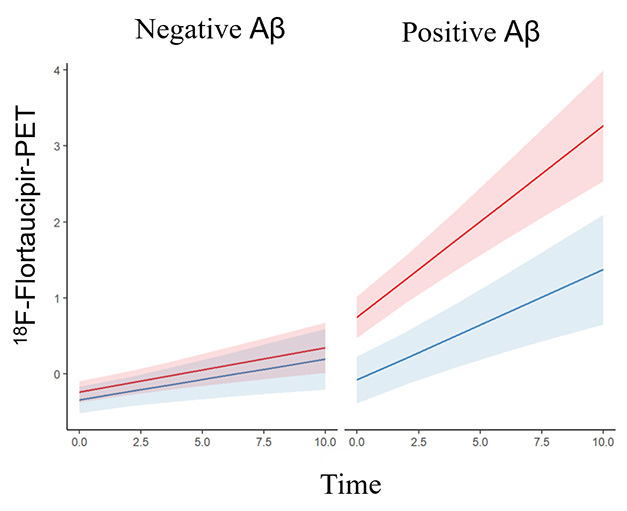
Although women suggest that they are particularly susceptible to tau pathology, scientists lack conclusive data. Currently, a meta-analysis of six longitudinal taupet studies provides the strongest evidence to date. In Jama Neurology on March 3, scientists led by Rachel Buckley at Massachusetts General Hospital in Charlestown reported that among people with amyloid plaques, some brain regions accumulated faster in women than men. Carrying the Apoe4 allele makes the spread of tangles in women even more eggs, regardless of the effects of amyloid.
- Among people with brain amyloid, tangles accumulate faster in women than in men.
- APOE4 also accelerated the accumulation of female tangles, but not male.
- Women may need to start amyloid immunotherapy earlier.
Findings imply that women may need to take anti-amyloid therapy at early stages of disease, but Buckley told Alzforum when women should begin treatment, or exactly what biological factors underlying this gender difference are unknown.
Nikolai Franzmeier and Dabina Beal of Ludwig Maximilian University in Munich called the data robust and persuasive. Pierre Talliot of the Banner Alzheimer's Disease Institute in Phoenix agreed. “The author makes the persuasive claim that women experience a more aggressive accumulation of tau than men,” Tariot wrote in Alzforum (comments below).

It's not the same. In amyloid-negative people (left), there is little entanglement accumulated over 10 years. In amyloid-positive (right), tangles grow faster in females (orange) than in males (blue). [Courtesy of Coughlan et al., American Medical Association, 2025.]
Most previous studies reporting higher tangle loads in women were cross-sections (February 2019 News; Buckley et al. , 2020; Edwards et al. , 2021). This left unanswered whether there were differences in accumulation, whether women were more resilient when tangled and therefore allowed higher loads at certain clinical stages. Several longitudinal taupet studies strengthened the former lawsuit, but these had fewer than 500 participants and in some cases not reaching statistical significance (Smith et al. , 2020; Jack et al. , 2020; Wang et al. , 2024).
To get a stronger answer, first author Gillian Cofran analyzed data from six longitudinal Tau Pet studies: the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, the Berkeley Aging Cohort Study, Biofinder 1, the Harvard Aging Brain Study, the Mayonnaise Clinic Study of Aging, and the Wisconsin Lineage of Alzheimer's. Overall, the meta-analysis consisted of 1,376 cognitively healthy participants at baseline. They were on average 72 years old, with 55% being female. All had baseline amyloid scans and multiple tau PET scans over an average of three years of time. Five studies used the Tau Tracer Flortaucipir, while Wrap used the MK-6240.
In the complete cohort, tangle accumulation was not altered by sex. Most people in this cognitively healthy cohort were amyloid-negative and had little change in taupet signal during the course of the study. However, of the 401 participants who tested positive for amyloid at baseline, that was a different story. Women were also entangled faster than men in the inferior temporal lobe, temporalis bruis, and lateral occipital cortex. “[These regions] Franzmeier and Biel pointed out.
Five studies using Flortaucipir showed that its effect was small, with women adding 0.001-0.020 SUVRs per year than men in these areas. In rap, the effect was large, varying from 0.037 SUVR for the temporal spindle-shaped gyri to 0.074 for the lateral occipital cortex. The MK-6240 is more sensitive than the Frolltauk pill, with a larger dynamic range, suggesting that this tracer may be able to better pick up small changes in the load of tangles.
At the other end of the scale, one study that showed no gender differences was BAC. The lowest amyloid-positive threshold was at 10 centiloid, with the oldest participant with mean baseline age of 76.
The author also looked for sex effects among APOE4 carriers. Here they discovered a subtle difference. Female E4 carriers accumulate more tangles in the inferior temporal lobe than in male carriers, even when considering amyloid loading. “It tells me that amyloid isn't the only driver,” Buckley pointed out. Animal studies show that the E4 allele can exacerbate tau pathology independently of amyloid (September 2017 News; October 2019 News; November 2023 News). Another recent study reported a stronger correlation between the number of APOE alleles and total tau levels in CSF, markers of neurodegeneration, and females than men (female than men) (Xu et al. , 2025).
Regarding the causes of this gender difference, previous studies involve hormonal changes during menopause or the effects of X-linked genes (Buckley et al. , 2022; May 2023 News; October 2022 News). Buckley plans to pursue both possibilities.
What does this mean for women's health? Fastest tangle accumulation may blunt the effectiveness of anti-amyloid immunotherapy in women. Trial data supports this. in Guntenermab In a phase 3 study, women had a higher baseline tangle load than men and did not obtain cognitive benefits from the drug (April 2023 Conference News). in Rekanemabu In the phase 3 exam, men also benefited more than women (December 2022 Conference News). However, Donanemab There were no gender differences in phase 3, where participants were selected by baseline entanglement load (July 2023 Conference News).
“The optimal threshold for initiating anti-Aβ immunotherapy may vary by gender, and early intervention in women may maximize clinical benefits,” Franzmeyer and Beale wrote in Alzform. That said, Talliot warned that other explanations may explain gender differences in the trial, including clear auxiliary pathology and drug use in female and male participants. Buckley agrees that further research is needed before making treatment recommendations. She wants to know when an intertwined accumulation first diverges between women and men. In the meantime, Buckley believes scientists need to consider stratifying baseline and outcome test data with sex.
News Quotes
- Is the female brain susceptible to tau pathology?
- apoe4 makes everything worse from start to finish
- In taopathy, apoe destroys neurons via microglia
- Does lipid shenanigans in APOE4 cause taopathy?
- Do you blame women's high tau for hormones?
- Ubiquitin peptidases associated with increased tau pathology in women
- What happens after amyloid plaque is removed? Who will benefit the most?
- Dare we say we have achieved a consensus: lekanemab slows down illness
- Donanemab data is fixed with bright data from AAIC
Treatment Quotes
Paper quote
-
Buckley RF, Scott MR, Hijacobs, Schultz AP, MJ Properties, Reed, RE, TJ Homan, Maebrim DV, ZB Ruebelstein, Manning L, Hansee BJ, Hansee EC, DM Rental, Johnson KA, Sparring RA.
Gender mediates the relationship between local tau pathology and cognitive decline.
Anne Newlor. November 2020; 88(5): 921-932. EPUB 2020 August 31st
PubMed. -
Edwards L, LA Joy R, Iacaccarino L, Strom A, Baker SL, Casalette KB, Covigo Y, Grant H, Kim M, Kramer JH, Mellinger TJ, Femme J, Postin KL, Rosen HJ, Soleimani – Magon DN, Wolf A, Miller BL.
Multimodal neural picture of gender differences in cognitive impairment patients with Alzheimer's disease continuum..
Neurobilool aging. September 2021: 86-98. EPUB 2021 April 22nd
PubMed. -
Smith R, Strandberg O, Mattsson-Carlgren N, Leuzy A, Palmqvist S, Pontecorvo MJ, Devous MD, Ossenkopple R, Hansson O.
Tau aggregate accumulation rates are higher in women and young amyloid-positive subjects.
brain. December 1, 2020; 143 (12): 3805-3815.
PubMed. -
Jack CR, Wiste HJ, Weigand SD, Therneau TM, Lowe VJ, Kantford J, Whitwell J, Josephs K, Schwarz CG, Black ML, Gunter JL, Petersen RC.
Predict future proportion of PET tau accumulation.
brain. October 1, 2020; 143 (10): 3136-3150.
PubMed. -
Wang YT, The Servaes S, Tissot C, Rahmuni N, Macedo AC, Fernandez-Arias. Initiative Newsletter.
The sex-specific regulation of amyloid-β in tau phosphorylation underlies faster accumulation of entanglements in women.
brain. April 4, 2024; 147(4): 1497-1510.
PubMed. -
Xu X, Kwon J, Yan R, Apio C, Song S, Heo G, Yang Q, Timsina J, Buddd J, Blennow K, Seriz A, Leain JL, Leevo JL, Demper AJ, Hohman TJ, Pastor P, Pesor P, Pes. Morris JC, Park T, Crucha C, Sung YJ.
Sexual differences in pathology of apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer's disease through ancestors..
Jama Netw Open. 2025 March 3rd; 8(3): E250562.
PubMed. -
Buckley RF, O'Donnell A, McGrath ER, Jacobs HI, Lois C, Satizabal CL, Ghosh S, Rubinstein ZB, Murabito JM, Sperling RA, Johnson KA, Seshadri S, Beiser As As As.
Menopause state reduces gender differences in tau burden: Framingham Pet Study.
Anne Newlor. July 2022; 92 (1): 11-22. EPUB 2022 May 17th
PubMed.
|
Sources 2/ https://www.alzforum.org/news/research-news/confirmed-women-accumulate-tangles-faster-do-men The mention sources can contact us to remove/changing this article |
What Are The Main Benefits Of Comparing Car Insurance Quotes Online
LOS ANGELES, CA / ACCESSWIRE / June 24, 2020, / Compare-autoinsurance.Org has launched a new blog post that presents the main benefits of comparing multiple car insurance quotes. For more info and free online quotes, please visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/the-advantages-of-comparing-prices-with-car-insurance-quotes-online/ The modern society has numerous technological advantages. One important advantage is the speed at which information is sent and received. With the help of the internet, the shopping habits of many persons have drastically changed. The car insurance industry hasn't remained untouched by these changes. On the internet, drivers can compare insurance prices and find out which sellers have the best offers. View photos The advantages of comparing online car insurance quotes are the following: Online quotes can be obtained from anywhere and at any time. Unlike physical insurance agencies, websites don't have a specific schedule and they are available at any time. Drivers that have busy working schedules, can compare quotes from anywhere and at any time, even at midnight. Multiple choices. Almost all insurance providers, no matter if they are well-known brands or just local insurers, have an online presence. Online quotes will allow policyholders the chance to discover multiple insurance companies and check their prices. Drivers are no longer required to get quotes from just a few known insurance companies. Also, local and regional insurers can provide lower insurance rates for the same services. Accurate insurance estimates. Online quotes can only be accurate if the customers provide accurate and real info about their car models and driving history. Lying about past driving incidents can make the price estimates to be lower, but when dealing with an insurance company lying to them is useless. Usually, insurance companies will do research about a potential customer before granting him coverage. Online quotes can be sorted easily. Although drivers are recommended to not choose a policy just based on its price, drivers can easily sort quotes by insurance price. Using brokerage websites will allow drivers to get quotes from multiple insurers, thus making the comparison faster and easier. For additional info, money-saving tips, and free car insurance quotes, visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ Compare-autoinsurance.Org is an online provider of life, home, health, and auto insurance quotes. This website is unique because it does not simply stick to one kind of insurance provider, but brings the clients the best deals from many different online insurance carriers. In this way, clients have access to offers from multiple carriers all in one place: this website. On this site, customers have access to quotes for insurance plans from various agencies, such as local or nationwide agencies, brand names insurance companies, etc. "Online quotes can easily help drivers obtain better car insurance deals. All they have to do is to complete an online form with accurate and real info, then compare prices", said Russell Rabichev, Marketing Director of Internet Marketing Company. CONTACT: Company Name: Internet Marketing CompanyPerson for contact Name: Gurgu CPhone Number: (818) 359-3898Email: cgurgu@internetmarketingcompany.BizWebsite: https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ SOURCE: Compare-autoinsurance.Org View source version on accesswire.Com:https://www.Accesswire.Com/595055/What-Are-The-Main-Benefits-Of-Comparing-Car-Insurance-Quotes-Online View photos
to request, modification Contact us at Here or collaboration@support.exbulletin.com



