Uncategorized
Climate change will make California’s massive earthquake even more devastating
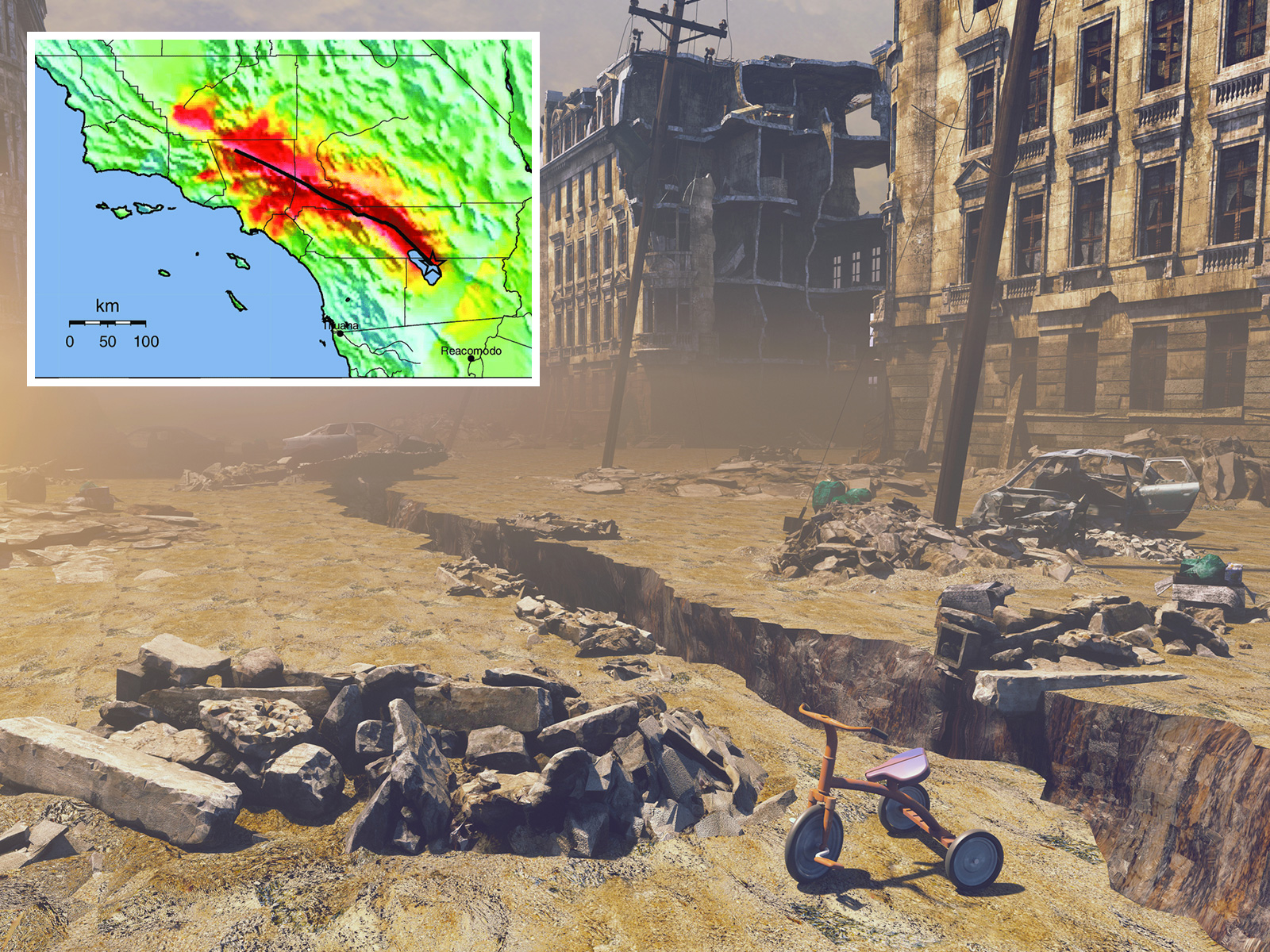
California is expected to experience the “Big One,” a massive earthquake along the San Andreas Fault, sometime in the next 100 years, as droughts linked to climate change parched many parts of the state, and wildfires and landslides risk bringing destruction. worst. It expects 2,000 deaths, 50,000 injuries, and $200 billion in economic damage
John J. Conlon was just a boy when a devastating earthquake struck San Francisco. But it was not only the earthquake itself of April 18, 1906, that shattered itself in his memory: the most shocking event came immediately.
“Subsequently, the events were referred to as ‘before’ or ‘after’ the fire,” he said in a San Francisco City Museum eyewitness account. “The earthquake, which was responsible for the fire, was a secondary matter. As a boy of seven, freed from parental control for three days, I enjoyed the excitement of the disastrous events around me without understanding their consequences.”
Now scientists are warning that these consequences could be more serious next time.
The “Big Earthquake,” a massive earthquake expected to strike California along the San Andreas fault, is expected sometime in the next 100 years, and experts warn that climate change could make the already deadly event worse.
With a magnitude of 8 or higher, a massive earthquake can cause widespread devastation for miles, specifically in densely populated cities like Los Angeles. Climate change has little effect on the cause of earthquakes. However, scientists note that global warming affects the forest fires and mudslides that follow an earthquake, and can multiply deaths and economic losses.
In this photomontage, an artist’s impression of a city ruins with a crack in the street and a “ShakeMap” is shown. The inset image represents the shaking generated by the earthquake scenario upon which the Great California ShakeOut was based. Colors represent modified Mercalli intensity, with warmer colors representing areas of greater damage. Getty/National Academy of Sciences What is “big”?
An earthquake of this magnitude over an 800-mile fault line could wreak havoc, destroying buildings, breaking life lines such as roads and canals, and causing thousands of deaths. The devastation is expected to be particularly bad for those in basin cities like Palm Springs, Los Angeles and San Francisco, according to SanAndreasFault.org, a fault line website.
Dozens of earthquakes happen every day, but many of them are so small that they can hardly be felt or not felt at all. An earthquake of magnitude 6 or greater is considered dangerous. California rarely experiences earthquakes close to magnitude 8, with historical records showing that the state may have experienced two earthquakes close to that magnitude – a magnitude 7.9 earthquake in 1857 and a magnitude 7.8 quake in 1906. Fourteenth century based on data points along fault lines.
Scientists aren’t sure exactly where or when the “big event” will happen, only that it will eventually happen and that people should prepare.
In 2008, seismologist Lucy Jones worked with a team of scientists to formulate the ShakeOut Scenario, a USGS story predicting the potential damage caused by a magnitude 7.8 earthquake. Jones’ ShakeOut Scenario predicts deaths and economic losses from a massive earthquake if only current preventive measures are in place.
The potential damage from climate change is magnified
If the earthquake occurred at the San Andreas Fault, ShakeOut’s scenario estimates up to 2,000 deaths, 50,000 injuries, and $200 billion in economic destruction as a result. Each aftershock, which can occur for months after the first earthquake, can add to these numbers.
The most dangerous part of an earthquake, apart from the tremors, are the fires that often start from urban sources after an earthquake. A large earthquake can break gas lines, damage electrical transformers, and cause power lines to fall to the ground. When electricity is restored, damaged infrastructure can cause fires that can be exacerbated by climate change.
In recent years, drought has dried out much of California and contributed to far-reaching wildfires that are difficult to control and take days, weeks or months to put out.
On Thursday, the Center for Climate and Energy Solutions published a drought monitoring map showing drought zones in the United States. Central and Southern California are among the hardest hit areas. The study said climate change increases the odds of exacerbating droughts by increasing evaporation rates, which leads to dry soils and reduced precipitation. The study finds that annual precipitation in the southwestern United States has decreased since the beginning of the 20th century and is expected to continue to decline.
If the area under the “Big One” had a drought at the time of the earthquake, the fires that followed the earthquake and every aftershock could be even more damaging. Jones told Newsweek that the 2008 ShakeOut scenario estimated that the quake would spark as many as 1,600 fires in addition to expected mass casualties and financial losses. If California experiences a severe drought like it has in recent years, the damage from the fires could be worse than expected.
“Climate change increases the likelihood that we will not have a cold, calm day and will have severe fire conditions,” Jones said. “In this case, [damage] It will more than double.”
Jones also told Newsweek that the greatest damage from the Big One would be expected if the quake occurred during the Santa Ana winds, which produce strong, dry winds across Southern California. Winds greatly increase the potential for fires, which are expected to multiply any fatalities and losses from the earthquake itself.
If the earthquake occurs during the winter months, landslides may occur. The Drought Study by the Center for Climate and Energy Solutions said climate models show that global warming contributes to severe droughts followed by periods of intense rainfall, which increases the likelihood of landslides.
“This creates the need to expand water storage during drought years and increases the risk of flooding and dam failure during periods of intense rainfall,” the study said.
Jones said landslides would be much less harmful than fires. The ShakeOut scenario estimates at least $100 billion in additional damage from the fires. Meanwhile, landslides can cause an additional $1 billion in damage.
The ShakeOut scenario that Jones created predicts that suffering will extend beyond the sheer number of injuries and deaths, as any road, path, pipe, or sewer line that crosses the fault will be cut off by the earthquake. Damage to the infrastructure may prevent emergency services from accessing the fires or there may not be any source of water to fight the fire.
People in affected areas will be without electricity and water for a month or more, and local businesses can collapse if the owners don’t have the resources to endure that long without care. Even those who work in businesses or homes that were constructed or modified to withstand such an earthquake may experience catastrophic clean-ups. The ShakeOut scenario predicts that even if those buildings don’t collapse, any unlocked items will fall to the ground and potentially break, resulting in residents facing a massive cleanup without water or electricity to help them.
Perspective view of California’s major faults, showing prediction probabilities estimated by the California Earthquake Prediction III Unified. The color bar shows the estimated percentage probability of an earthquake of magnitude 6.7 or greater occurring in the next 30 years, as of 2014. Note that almost the entire San Andreas system is red on the probability scale due to the inability of large earthquakes during and prior to the last century. USGS
Five major passes pass through the San Andreas Fault, including the Cajon Pass and Interstate 10. The passes are referred to as “lifeline lanes”, as many mountains around Los Angeles block roads from crossing into the area. Affected areas will need to find alternative sources of water and may be cut off from surrounding civilizations.
“It’s harder to fix these things and get them back to normal when the area is larger,” USGS geophysicist Morgan Page told Newsweek.
According to the ShakeOut scenario, when the “Big One” occurs, it will likely differ from the scenario presented since each earthquake “produces its own patterns of vibration and damage.”
“However, the broad regional effects will be similar, as will the long-term social and economic effects,” the scenario said.
The potential impact also varies depending on where the earthquake occurred. If it happened near Los Angeles, the sandy basin those cities were built upon would add to the damage. The volume of movement of cities built on sand beds is much greater than that of those built on more solid foundations, causing more buildings to collapse.
“Imagine you’re sitting on top of a solid rock and it jiggles,” Page told Newsweek. “It doesn’t move as much as if you put the same structure on top of the sand.”
How do you predict it?
The terrifying prospect of an earthquake of such devastating magnitude is influencing scientists and civilians to look for patterns and any means of preparing for when it strikes. However, Jones said that it is impossible to predict the “big one”.
Page told Newsweek that current models show that an earthquake of magnitude 8 or higher has a 7 percent chance of occurring in the next 30 years. Page said the predictions are based on fault lines along the San Andreas Fault that are prone to blowouts. One of the regions that ruptured in 1857 tends to rupture every 150 years, which indicates that it was one year late. Meanwhile, another area that experienced a devastating rupture in 1700 is liable to erupt every 300 years.
“Scientists don’t like it being random. We want to find a pattern,” Jones said. “[Common] The human emotion is to find a pattern about things that are dangerous and try to make a pattern of how to be safe. However, we haven’t found a really consistent pattern.”
Jones added that scientists often argue about time-dependent probabilities, by studying the dates of past earthquakes to formulate prediction models. However, it misses the “completely random” end of the spectrum. The only time-related probabilities you track are that the earthquake is expected to occur in the next century and not in the next year or decade.
Prepare
Although Jones said there is no way to prevent the “Big One,” there are ways that vulnerable areas can better prepare for the devastation.
Page and Jones suggested preventative measures such as retrofitting vulnerable structures, such as unreinforced masonry buildings or soft-storey buildings where the first floor of an apartment building sits with apartments stacked on top. The empty space on the lower level is not as strong as the rooms above and is more likely to collapse.
Smaller actions can also be taken, such as stockpiling water, increasing volunteer preparedness, and crafting collaborative plans.
“It’s really up to us to make sure the buildings and infrastructure are safe and reliable when that happens or we’re going to have a much tougher time,” Page said. “An earthquake is inevitable but our response to an earthquake is not. We can control how safe our buildings and infrastructure are.”
|
Sources 2/ https://www.newsweek.com/climate-change-make-massive-california-earthquake-even-more-devastating-1766478 The mention sources can contact us to remove/changing this article |
What Are The Main Benefits Of Comparing Car Insurance Quotes Online
LOS ANGELES, CA / ACCESSWIRE / June 24, 2020, / Compare-autoinsurance.Org has launched a new blog post that presents the main benefits of comparing multiple car insurance quotes. For more info and free online quotes, please visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/the-advantages-of-comparing-prices-with-car-insurance-quotes-online/ The modern society has numerous technological advantages. One important advantage is the speed at which information is sent and received. With the help of the internet, the shopping habits of many persons have drastically changed. The car insurance industry hasn't remained untouched by these changes. On the internet, drivers can compare insurance prices and find out which sellers have the best offers. View photos The advantages of comparing online car insurance quotes are the following: Online quotes can be obtained from anywhere and at any time. Unlike physical insurance agencies, websites don't have a specific schedule and they are available at any time. Drivers that have busy working schedules, can compare quotes from anywhere and at any time, even at midnight. Multiple choices. Almost all insurance providers, no matter if they are well-known brands or just local insurers, have an online presence. Online quotes will allow policyholders the chance to discover multiple insurance companies and check their prices. Drivers are no longer required to get quotes from just a few known insurance companies. Also, local and regional insurers can provide lower insurance rates for the same services. Accurate insurance estimates. Online quotes can only be accurate if the customers provide accurate and real info about their car models and driving history. Lying about past driving incidents can make the price estimates to be lower, but when dealing with an insurance company lying to them is useless. Usually, insurance companies will do research about a potential customer before granting him coverage. Online quotes can be sorted easily. Although drivers are recommended to not choose a policy just based on its price, drivers can easily sort quotes by insurance price. Using brokerage websites will allow drivers to get quotes from multiple insurers, thus making the comparison faster and easier. For additional info, money-saving tips, and free car insurance quotes, visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ Compare-autoinsurance.Org is an online provider of life, home, health, and auto insurance quotes. This website is unique because it does not simply stick to one kind of insurance provider, but brings the clients the best deals from many different online insurance carriers. In this way, clients have access to offers from multiple carriers all in one place: this website. On this site, customers have access to quotes for insurance plans from various agencies, such as local or nationwide agencies, brand names insurance companies, etc. "Online quotes can easily help drivers obtain better car insurance deals. All they have to do is to complete an online form with accurate and real info, then compare prices", said Russell Rabichev, Marketing Director of Internet Marketing Company. CONTACT: Company Name: Internet Marketing CompanyPerson for contact Name: Gurgu CPhone Number: (818) 359-3898Email: [email protected]: https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ SOURCE: Compare-autoinsurance.Org View source version on accesswire.Com:https://www.Accesswire.Com/595055/What-Are-The-Main-Benefits-Of-Comparing-Car-Insurance-Quotes-Online View photos
to request, modification Contact us at Here or [email protected]



