Health
Clues link premature infants with bowel disease and brain injury
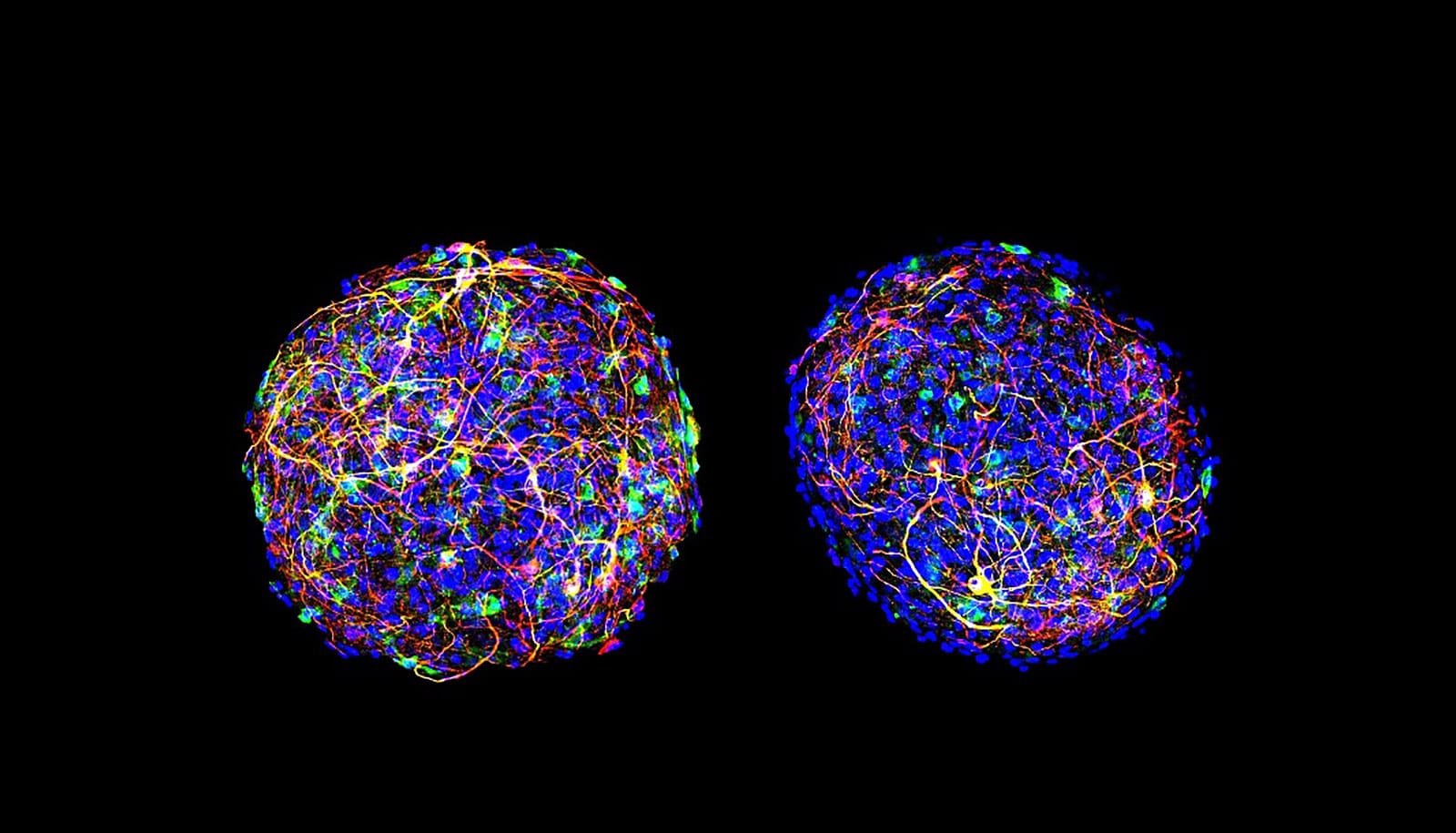
New studies may reveal a link between necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants and the development of severe brain injury in survivors.
Little is known about how the diseased gut “transmits” its devastation to the newborn’s brain.
Researchers are now using mice to identify missing links. Immune system cells say they move from the intestine to the brain and attack the cells, rather than protecting them as they normally would.
Team findings will be displayed in the journal Scientific translation medicine..
Necrotizing enterocolitis is life-threatening
Also found in 12% of babies Measurement Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), which weighs less than 3.5 pounds at birth, is a rapidly developing gastrointestinal emergency in which bacteria invade the walls of the colon, causing inflammation and ultimately destroying healthy tissue at the site. There is likely to be.When a sufficient number of cells die and puncture the intestinal wall, bacteria can enter the bloodstream and be life-threatening. Sepsis..
In a 2018 mouse study, researchers at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center found that NEC animals bind to intestinal bacteria and promote intestinal destruction with Toll-like receptors 4 (TLR4). I discovered that it makes a protein called. They also confirmed that TLR4 simultaneously activates immune cells in the brain known as microglia, causing white matter loss, brain damage, and cognitive decline. What wasn’t clear was how the two were connected.
In this latest study, researchers speculated that CD4 + T lymphocytes (immune system cells, also known as helper T cells) may be involved. CD4 + T cells help another type of immune cell, called a B lymphocyte (or B cell), to respond to the surface proteins (antigens) of cells infected with foreign invaders such as bacteria and viruses. It will be given a “helper” nickname. Immature B cells activated by CD4 + T cells are plasma cells that produce antibodies that mark the infected cells for disposal from the body, or antigens for a faster response to future invasion. It becomes one of the memory cells that “remembers” biochemistry.
CD4 + T cells also deliver chemical mediators that carry another type of T cell, known as a killer T cell, to that area so that the infected cells can be eliminated. However, if this activity occurs at the wrong place or at the wrong time, the signal can mistakenly tell the killer T cells to attack healthy cells.
“Comparing the brains of NEC infants with those of infants who died from other causes, we found that the former had accumulated CD4 + T cells and increased microglial activity,” said Johns, chief surgeon. Said David Hackham, the lead author of the study. Professor of Surgery at Hopkins Children’s Center and Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. “These T cells were suspected to be derived from the NEC inflamed area of the intestine and we attempted to prove it using neonatal mice as a model of what happens in human infants.”
Brain injury
At the beginning of a series of experiments, researchers induced NEC in infant mice and examined the brain. As expected, the tissue showed a significant increase in CD4 + T cells and high levels of protein associated with increased microglial activity. In a follow-up study, researchers showed that the blood-brain barrier in NEC mice was weakened. This is usually a biological barrier that prevents bacteria, viruses, and other dangerous substances that circulate in the bloodstream from reaching the central nervous system. Researchers speculate that this could explain how CD4 + T cells from the intestine migrate to the brain.
Next, the researchers determined that the accumulation of CD4 + T cells was the cause of the brain damage seen at NEC. They did this by first biologically blocking the migration of helper T cells to the brain, and then in another experiment neutralized the T cells by binding to a specially designed antibody. .. In both cases, microglial activity was suppressed and white matter in the brain was preserved.
To further clarify the role of CD4 + T cells in brain injury, researchers used NEC to collect T cells from the mouse brain and raise them to lack both T and B lymphocytes. It was injected into the brain of a mouse. Mice that received lymphocytes had higher levels of chemical signals that attracted killer T cells compared to control mice that did not receive any T cells. Researchers also observed markers of brain damage, including microglial activation, brain inflammation, and white matter loss.
Organoid white matter
Researchers then found out how the accumulating CD4 + T cells destroy the white matter, a fat called myelin that actually covers and protects neurons in the brain and promotes communication between them. I tried to better define. To do this, they used organoids, laboratory-grown mouse brain cells, to simulate the entire brain. NEC mouse brain-derived CD4 + T cells were added to these laboratory “mini brains” and tested for several weeks.
Hackam and his colleagues found that as the amount of myelin decreased, certain chemical signals from T cells (a cytokine (inflammatory protein) known as interferon gamma (IFN gamma)) increased in organoids. .. This activity was not seen in organoids that received CD4 + T cells from NEC-free mice.
After adding only IFN-γ to the organoids, the researchers saw the same levels of increased inflammation and decreased myelin as seen in NEC mice. When they added IFN-γ neutralizing antibodies, cytokine production was significantly reduced, inflammation was suppressed, and white matter was partially restored.
Researchers conclude that IFN-γ directs the processes leading to NEC-related brain damage. Examination of the brain tissue of NEC mice confirmed their findings when higher levels of IFN-γ were revealed than in disease-free mouse tissue.
Genetic clues to NEC
Next, the researchers investigated whether CD4 + T cells could migrate from the intestine to the brain of NEC mice. To do this, they obtained CD4 + T cells from the intestines of infant mice with and without NEC. Both types of cells were injected into the brains of infant mice in two groups. One is a set that can produce the protein Rag1 and the other is a set that cannot. Rag1-deficient mice do not have mature T or B lymphocytes.
Rag1-deficient mice treated with intestinal helper T cells from NEC mice showed the same brain injury characteristics as seen in previous experiments. Both T cells in mice with and without NEC did not cause brain damage in mice with Rag1 and did not cause T cells in mice without NEC in Rag1-deficient mice. This showed that intestinal helper T cells from NEC mice were the only ones that could cause brain damage.
In the second test, mouse intestinal T cells, with or without NEC, were injected into the peritoneum (the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity) of Rag1-deficient mice. Only NEC mouse intestinal T cells caused brain damage.
The team confirmed this finding by sequencing the same portion of both brain- and intestinal-derived T lymphocytes from mice with and without NEC. The sequences of helper T cells from mice with NEC were on average 25% genetically similar, while those from mice without NEC were only 2% similar.
In the final experiment, the researchers blocked only IFN-γ. Doing so provided significant protection against the development of brain injury in severe NEC mice. This suggests a therapeutic approach that may benefit premature infants in this condition, the researchers say.
“Our research strongly suggests that helper T cells from the intestine inflamed by NEC can migrate to the brain and cause damage,” says Hackham. “Since the mouse model in our study has previously been shown to be closely consistent with what happens in humans, we believe this is a possible mechanism by which NEC-related brain injury can occur in premature babies. I am. “
Based on these findings, Hackham says that measures to prevent this type of brain injury may be possible, including treatments that block the action of INF-γ.
Additional researchers from Johns Hopkins and the University of Lausanne contributed to the study and were funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Hackam and two other co-authors have patents on NEC treatment that are not related to the study in this study. Other authors have not declared competing interests.
Source: Johns Hopkins University
What Are The Main Benefits Of Comparing Car Insurance Quotes Online
LOS ANGELES, CA / ACCESSWIRE / June 24, 2020, / Compare-autoinsurance.Org has launched a new blog post that presents the main benefits of comparing multiple car insurance quotes. For more info and free online quotes, please visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/the-advantages-of-comparing-prices-with-car-insurance-quotes-online/ The modern society has numerous technological advantages. One important advantage is the speed at which information is sent and received. With the help of the internet, the shopping habits of many persons have drastically changed. The car insurance industry hasn't remained untouched by these changes. On the internet, drivers can compare insurance prices and find out which sellers have the best offers. View photos The advantages of comparing online car insurance quotes are the following: Online quotes can be obtained from anywhere and at any time. Unlike physical insurance agencies, websites don't have a specific schedule and they are available at any time. Drivers that have busy working schedules, can compare quotes from anywhere and at any time, even at midnight. Multiple choices. Almost all insurance providers, no matter if they are well-known brands or just local insurers, have an online presence. Online quotes will allow policyholders the chance to discover multiple insurance companies and check their prices. Drivers are no longer required to get quotes from just a few known insurance companies. Also, local and regional insurers can provide lower insurance rates for the same services. Accurate insurance estimates. Online quotes can only be accurate if the customers provide accurate and real info about their car models and driving history. Lying about past driving incidents can make the price estimates to be lower, but when dealing with an insurance company lying to them is useless. Usually, insurance companies will do research about a potential customer before granting him coverage. Online quotes can be sorted easily. Although drivers are recommended to not choose a policy just based on its price, drivers can easily sort quotes by insurance price. Using brokerage websites will allow drivers to get quotes from multiple insurers, thus making the comparison faster and easier. For additional info, money-saving tips, and free car insurance quotes, visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ Compare-autoinsurance.Org is an online provider of life, home, health, and auto insurance quotes. This website is unique because it does not simply stick to one kind of insurance provider, but brings the clients the best deals from many different online insurance carriers. In this way, clients have access to offers from multiple carriers all in one place: this website. On this site, customers have access to quotes for insurance plans from various agencies, such as local or nationwide agencies, brand names insurance companies, etc. "Online quotes can easily help drivers obtain better car insurance deals. All they have to do is to complete an online form with accurate and real info, then compare prices", said Russell Rabichev, Marketing Director of Internet Marketing Company. CONTACT: Company Name: Internet Marketing CompanyPerson for contact Name: Gurgu CPhone Number: (818) 359-3898Email: [email protected]: https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ SOURCE: Compare-autoinsurance.Org View source version on accesswire.Com:https://www.Accesswire.Com/595055/What-Are-The-Main-Benefits-Of-Comparing-Car-Insurance-Quotes-Online View photos
Pictures Credit
to request, modification Contact us at Here or [email protected]



