Health
Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 viral load in inpatients
Due to the rapid spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Virus Type 2 (SARS-CoV-2) worldwide, sensitive and specific diagnostic kits are being rapidly developed. Primarily, these test kits are based on the reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for detecting total viral ribonucleic acid (RNA). One limitation of RT-PCR testing is that as the infection progresses over time, the relationship between positive RT-PCR and viral infectivity becomes less pronounced.

Transmission electron micrograph of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles (UK B.1.1.7 variant) isolated from patient samples and cultured in cell culture. Image taken at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland. Credit: NIAID
Previous studies have shown that SARS-CoV-2 remains in the upper respiratory tract for approximately 14.5 days after the onset of disease symptoms. However, many studies have reported the presence of viral RNA weeks, long before most people were infected. For this reason, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has created new guidelines for isolation prevention measures.
According to previous guidelines, the quarantine period for mild to moderately infected individuals was 10 days after the onset of symptoms, based on studies of viral infectivity in clinical samples. For severely infected patients or immunocompromised conditions, quarantine for up to 20 days was recommended. However, current studies show that some immunosuppressed patients may remain contagious for several weeks, regardless of their symptoms. This observation makes it difficult to formulate a strategy for isolation based on the symptoms of the disease.
It is difficult to stop the spread of the infection because there is no fast, high-throughput testing system to distinguish between sick and healthy people. The methods available to determine infectivity are time consuming and impractical. As a result, scientists are interested in discovering molecular markers that may correlate with infectivity. With this excuse, they used SARS-CoV-2 total RNA (positive and negative strands) and subgenomic RNA (nucleocapsid (N), spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and six accessory proteins). I studied. ). Subgenomic RNA can be distinguished from total RNA by placing alternative PCR primers. Evaluation of subgenomic RNA dynamics during infection revealed the absence of subgenomic RNA in the throat of SARS-CoV-2 patients up to 5 days after the onset of symptoms. Little information is available on subgenomic RNA kinetics in inpatients and immunosuppressed patients with severe COVID-19 infection.
New paper published in medRxiv* Preprint server, investigating the role of subgenomic RNA transcripts in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Previously, scientists believed that subgenomic RNA could be a traceable infectious marker for monitoring infectivity. In the current study, RT-PCR was used to amplify whole and subgenome nucleoprotein genes (N) and envelope genes (E). Nasopharyngeal samples were collected from 190 patients admitted in Michigan between March 13, 2020 and June 10, 2020.
Researchers have observed a strong correlation between total RNA and subgenomic RNA. They found that the time points after the onset of symptoms were the same, and that the reduction in infection rate was the same for both total RNA and subgenomic RNA. The predictability of subgenomic copy numbers from total copy numbers indicates that recognition of subgenomic RNA does not add additional information about infectivity beyond that obtained from total copy numbers alone. As a result, scientists conclude that there is no additional benefit in assessing subgenomic RNA.
In this study, scientists found that negative subgenome E RT-PCR was positively correlated with the time the patient was uninfected. Therefore, subgenome E is not a valid marker for predicting the infectivity of the virus. The study also found that the median number of days from the onset of symptoms to the negative subgenome NRT-PCR was 25 days. Therefore, the use of subgenome N as a marker of infectivity significantly prolongs quarantine and is unpredictable. This difference may be due to the higher expression levels of subgenome N compared to subgenome E.
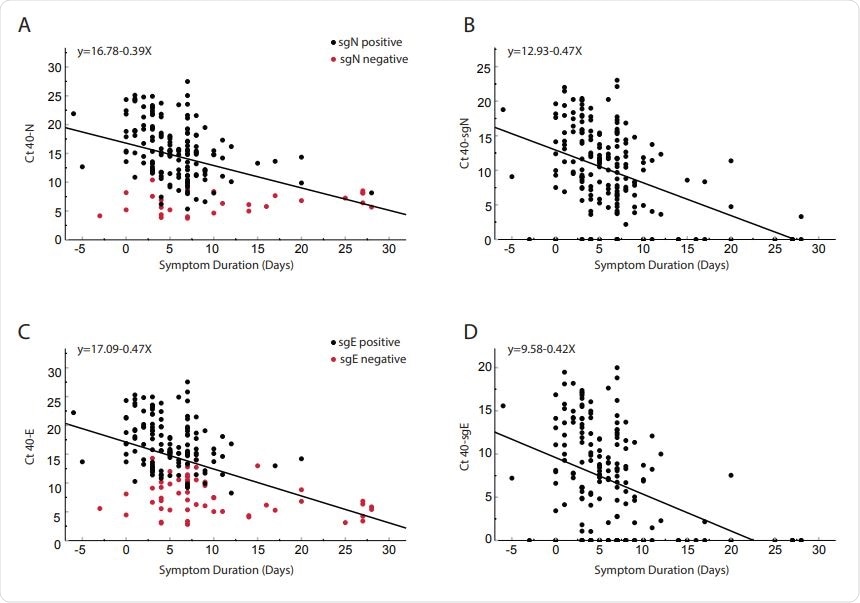
Comparison of cycle thresholds and days since symptom onset of clinical samples from 185 inpatients. Total N (Panel A), Subgenome N (Panel B), Total E (Panel C), and Subgenome E (Panel D). Red dots on panels A and C represent negative samples of the subgenome, and black dots represent positive samples of the subgenome. Of the 185 patients, 56 were negative for sgE and 28 were negative for sgN (shown on the y-axis). Pearson correlation coefficient: N = -0.404 p <0.0001; SgN = -0.466, p <0.0001; E = -0.456 p <0.0001; sgE = -0.427 <0.0001. The linear regression linear equation is shown in each panel.
Previous studies have shown that subgenomic RNA is a good marker for active infection because it degrades more rapidly than total RNA without replication. This result was inconsistent with the results obtained in the current study. The difference in this result is not due to the difference in degradation of the subgenome transcript and the whole transcript, but due to the difference in the detection of the transcript.
Studies conclude that determination of infectivity by evaluation of subgenomic RNA is not recommended. Similarly, for non-immunosuppressed patients, the total RNA copy number threshold provides the same information that can be obtained from total RNA copy number. One limitation of current research is that scientists have not isolated the virus from hospital samples and have not correlated it with total copy number or subgenome copy number. Only the correlation between transcripts and symptom duration has been used as a determinant of infectivity.
*Important Notices
medRxiv Publish preliminary scientific reports that should not be considered definitive as they are not peer-reviewed, guide clinical practice / health-related behaviors, and should not be treated as established information.
Journal reference:
- SARS-CoV-2 total and subgenomic RNA viral load in inpatients, Derek E. Dimcheff, Andrew L. Valesano, Kalee E. Rumfelt, William J. Fitzsimmons, Christopher Blair, Carmen Mirabelli, Joshua G. Petrie, Emily T. Martin , Chandan Bhambhani, Muneesh Tewari, Adam S. Lauring medRxiv 2021.02.25.21252493; Doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.25.21252493, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.02.25.21252493v1
..
What Are The Main Benefits Of Comparing Car Insurance Quotes Online
LOS ANGELES, CA / ACCESSWIRE / June 24, 2020, / Compare-autoinsurance.Org has launched a new blog post that presents the main benefits of comparing multiple car insurance quotes. For more info and free online quotes, please visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/the-advantages-of-comparing-prices-with-car-insurance-quotes-online/ The modern society has numerous technological advantages. One important advantage is the speed at which information is sent and received. With the help of the internet, the shopping habits of many persons have drastically changed. The car insurance industry hasn't remained untouched by these changes. On the internet, drivers can compare insurance prices and find out which sellers have the best offers. View photos The advantages of comparing online car insurance quotes are the following: Online quotes can be obtained from anywhere and at any time. Unlike physical insurance agencies, websites don't have a specific schedule and they are available at any time. Drivers that have busy working schedules, can compare quotes from anywhere and at any time, even at midnight. Multiple choices. Almost all insurance providers, no matter if they are well-known brands or just local insurers, have an online presence. Online quotes will allow policyholders the chance to discover multiple insurance companies and check their prices. Drivers are no longer required to get quotes from just a few known insurance companies. Also, local and regional insurers can provide lower insurance rates for the same services. Accurate insurance estimates. Online quotes can only be accurate if the customers provide accurate and real info about their car models and driving history. Lying about past driving incidents can make the price estimates to be lower, but when dealing with an insurance company lying to them is useless. Usually, insurance companies will do research about a potential customer before granting him coverage. Online quotes can be sorted easily. Although drivers are recommended to not choose a policy just based on its price, drivers can easily sort quotes by insurance price. Using brokerage websites will allow drivers to get quotes from multiple insurers, thus making the comparison faster and easier. For additional info, money-saving tips, and free car insurance quotes, visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ Compare-autoinsurance.Org is an online provider of life, home, health, and auto insurance quotes. This website is unique because it does not simply stick to one kind of insurance provider, but brings the clients the best deals from many different online insurance carriers. In this way, clients have access to offers from multiple carriers all in one place: this website. On this site, customers have access to quotes for insurance plans from various agencies, such as local or nationwide agencies, brand names insurance companies, etc. "Online quotes can easily help drivers obtain better car insurance deals. All they have to do is to complete an online form with accurate and real info, then compare prices", said Russell Rabichev, Marketing Director of Internet Marketing Company. CONTACT: Company Name: Internet Marketing CompanyPerson for contact Name: Gurgu CPhone Number: (818) 359-3898Email: cgurgu@internetmarketingcompany.BizWebsite: https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ SOURCE: Compare-autoinsurance.Org View source version on accesswire.Com:https://www.Accesswire.Com/595055/What-Are-The-Main-Benefits-Of-Comparing-Car-Insurance-Quotes-Online View photos
Pictures Credit
to request, modification Contact us at Here or collaboration@support.exbulletin.com



