Health
Analysis correlates COVID-19 with microvascular injury and inflammation in the brain
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic is caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-2 (SARS-CoV-2), an RNA virus belonging to the Coronaviridae family. Studies show that patients with 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) often suffer from neurological disorders such as stroke, loss of taste and smell, amnesia, confusion, and delirium.
By comparing symptoms associated with other coronavirus infections, researchers predicted the potential for cognitive dysfunction in COVID-19 patients.
For example, researchers found that both viruses belonged to the Coronaviridae family during the outbreak of SARS-CoV-1 in 2002 and the outbreak of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) in 2012, with 20% of patients recovering from memory. I observed that I was suffering from a disability. Given all recent evidence, researchers predict the risk of a potential surge in neurocognitive deficits such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
People with dementia, such as vascular dementia, AD, or presenile dementia, are more likely to be infected with SARS-CoV-2 than people without the disease. In addition, some of the most common symptoms in COVID-19 patients with dementia are active delirium, cognitive decline, and increased mortality.
Researchers have also shown that COVID-19 infection leads to diminished neuropsychological assessments such as inattention, agitation, confusion, and disorientation.
A recent study of 236,000 individuals recovered from COVID-19 found that patients requiring hospitalization, ICU admission, or suffering from encephalopathy were at increased risk of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Proven. However, another study involving COVID-19 patients with mild to moderate symptoms who did not require hospitalization also showed mental health and neurocognitive impairment.
Some studies have shown that SARS-CoV-2 can infect the brain via the olfactory bulb, but other studies have found that the virus is not found in the brain or cerebrospinal fluid. The virus has also been reported to cause inflammation of the central nervous system (CNS) and damage to microvessels. Scientists have shown that the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein freely crosses the blood-brain barrier (BBB), triggering an inflammatory response in microvascular endothelial cells and causing BBB dysfunction.
New research published in the journal Research and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease We analyzed the relationship between COVID-19 infection and cerebral microvascular injury and neuroinflammation.
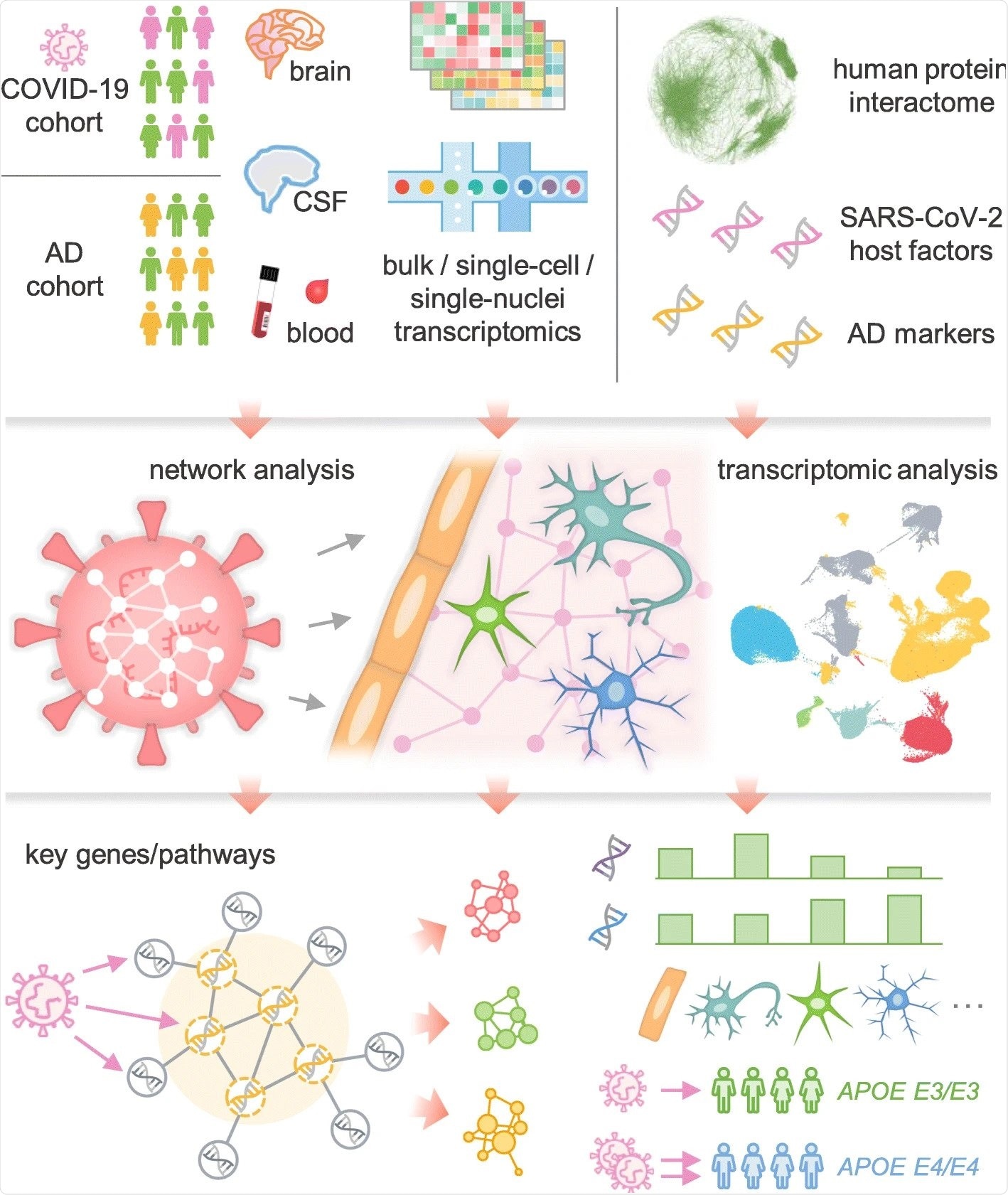
![Diagram showing a network-based multimodal omics analysis framework. The transcriptome (both bulk and unicellular or mononuclear) of COVID-19 (blood and cerebrospinal fluid) patients was examined. [CSF] Sample) or Alzheimer's disease (AD) (brain sample). We also edited a 10 SARS-CoV-2 host (human) factor dataset based on the CRISPR-Cas9 assay or protein-protein interaction assay, AD blood and CSF markers, and neurological disorder-related genes / proteins. Network proximity analysis of human protein-protein interactions was used to investigate network-based associations between SARS-CoV-2 host factors and several selected neurological disorders. To understand the potential mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 affects the brain, including direct brain invasion, neuroinflammation, and microvascular injury, (1) altered expression of AD markers in COVID-19 patients, ( 2) SARS-CoV-2 host factors in AD patients and healthy individuals at the tissue, brain region, and single cell / nuclear levels. These transcriptomics analyzes involved network analysis to uncover potential mechanisms (key genes or pathways) involved in protein-protein interactions. Diagram showing a network-based multimodal omics analysis framework. The transcriptome (both bulk and unicellular or mononuclear) of COVID-19 (blood and cerebrospinal fluid) patients was examined. [CSF] Sample) or Alzheimer's disease (AD) (brain sample). We also edited a 10 SARS-CoV-2 host (human) factor dataset based on the CRISPR-Cas9 assay or protein-protein interaction assay, AD blood and CSF markers, and neurological disorder-related genes / proteins. Network proximity analysis of human protein-protein interactions was used to investigate network-based associations between SARS-CoV-2 host factors and several selected neurological disorders. To understand the potential mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 affects the brain, including direct brain invasion, neuroinflammation, and microvascular injury, (1) altered expression of AD markers in COVID-19 patients, ( 2) SARS-CoV-2 host factors in AD patients and healthy individuals at the tissue, brain region, and single cell / nuclear levels. These transcriptomics analyzes involved network analysis to uncover potential mechanisms (key genes or pathways) involved in protein-protein interactions.](https://i0.wp.com/d2jx2rerrg6sh3.cloudfront.net/image-handler/picture/2021/6/ezgif-3-66df372a0cfc.jpg?resize=740%2C877&ssl=1)
Diagram showing a network-based multimodal omics analysis framework. The transcriptome (both bulk and unicellular or mononuclear) of COVID-19 (blood and cerebrospinal fluid) patients was examined. [CSF] Sample) or Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (brain sample). We also edited a 10 SARS-CoV-2 host (human) factor dataset based on the CRISPR-Cas9 assay or protein-protein interaction assay, AD blood and CSF markers, and neurological disorder-related genes / proteins. Network proximity analysis of human protein-protein interactions was used to investigate network-based associations between SARS-CoV-2 host factors and several selected neurological disorders. To understand the potential mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 affects the brain, including direct brain invasion, neuroinflammation, and microvascular injury, (1) altered expression of AD markers in COVID-19 patients, ( 2) SARS-CoV-2 host factors in AD patients and healthy individuals at the tissue, brain region, and single cell / nuclear levels. These transcriptomics analyzes involved network analysis to uncover potential mechanisms (key genes or pathways) involved in protein-protein interactions.
Researchers in the current study found that the SARS-CoV-2 host factor is a comprehensive protein-protein interaction (PPI).) Proteins associated with networks and specific neurological functions are directly or indirectly targeted by the virus through the PPI, which contains the viral host factor. This study found limited evidence to link direct brain and neuronal damage to COVID-19 infection. However, considerable research is available focusing on the molecular pathways associated with neuroinflammation and cerebral microvascular injury in COVID-19 patients.
To conduct fair studies related to pathophysiological pathways, the researchers in this study have procured a multimodal omics dataset for COVID-19 patients. The data include bulk and single cell / nuclear transcriptomics, proteomics, and interactive PPIs. Current research is investigating the relationship between drugs or drug targets and diseases using network-based drugs and diseases and disease-to-disease proximity methods. This was done to shed light on the understanding of the pathological mechanism of cognitive dysfunction after COVID-19 infection. This will help determine new targets for the development of effective treatments.
The mechanisms behind the adverse effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on CNS, which increase the likelihood of developing dementia such as AD, have been studied. Researchers have documented some of the genes encoding proteins associated with AD, such as RAB7A, TGFB1, and VCAM1. According to the degree and centrality of the eigenvectors, these proteins show greater influence on the network. In addition, based on the transcriptomics analysis profile, these genes were found to be altered in COVID-19 patients.
To investigate the potential for SARS-CoV-2 to invade the brain directly, this study is a key factor that may contribute to tissue, brain region, and brain cell type infections by SARS-CoV-2. I studied the expression of.
The low expression of was revealed. TMPRSS2 Neuron and brain ACE2. Researchers argued that SARS-CoV-2 is very unlikely to invade target neurons directly via ACE2. However, the virus can enter the brain through the cerebral endothelium using receptors such as BSG and NRP.In addition, previous studies have shown that HCoV (humans) Coronavirus) In the human brain.
Several AD marker genes, such as GSTM3, TGFB1, and TNFRSF1B, have been identified in the current study. These genes were altered in COVID-19 patients. Network analysis revealed that these genes are enriched in the PPIs of immune-related gene products such as ITGB1 and ARRB2. In addition, the study identified genes such as STAT3 and JAK1 and found that the JAK-STAT signaling pathway is associated with inflammation in COVID-19 patients.
One of the limitations of current research is to consider the expression levels of major SARS-CoV-2 invaders. ACE2 And TMPRSS2However, the virus can target the brain directly through an unknown mechanism. Scientists need more research considering genetic aspects and multimodal omics data from individuals with AD and infected with COVID-19, leaving room for further analysis of network-based findings. Clarified.
..
What Are The Main Benefits Of Comparing Car Insurance Quotes Online
LOS ANGELES, CA / ACCESSWIRE / June 24, 2020, / Compare-autoinsurance.Org has launched a new blog post that presents the main benefits of comparing multiple car insurance quotes. For more info and free online quotes, please visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/the-advantages-of-comparing-prices-with-car-insurance-quotes-online/ The modern society has numerous technological advantages. One important advantage is the speed at which information is sent and received. With the help of the internet, the shopping habits of many persons have drastically changed. The car insurance industry hasn't remained untouched by these changes. On the internet, drivers can compare insurance prices and find out which sellers have the best offers. View photos The advantages of comparing online car insurance quotes are the following: Online quotes can be obtained from anywhere and at any time. Unlike physical insurance agencies, websites don't have a specific schedule and they are available at any time. Drivers that have busy working schedules, can compare quotes from anywhere and at any time, even at midnight. Multiple choices. Almost all insurance providers, no matter if they are well-known brands or just local insurers, have an online presence. Online quotes will allow policyholders the chance to discover multiple insurance companies and check their prices. Drivers are no longer required to get quotes from just a few known insurance companies. Also, local and regional insurers can provide lower insurance rates for the same services. Accurate insurance estimates. Online quotes can only be accurate if the customers provide accurate and real info about their car models and driving history. Lying about past driving incidents can make the price estimates to be lower, but when dealing with an insurance company lying to them is useless. Usually, insurance companies will do research about a potential customer before granting him coverage. Online quotes can be sorted easily. Although drivers are recommended to not choose a policy just based on its price, drivers can easily sort quotes by insurance price. Using brokerage websites will allow drivers to get quotes from multiple insurers, thus making the comparison faster and easier. For additional info, money-saving tips, and free car insurance quotes, visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ Compare-autoinsurance.Org is an online provider of life, home, health, and auto insurance quotes. This website is unique because it does not simply stick to one kind of insurance provider, but brings the clients the best deals from many different online insurance carriers. In this way, clients have access to offers from multiple carriers all in one place: this website. On this site, customers have access to quotes for insurance plans from various agencies, such as local or nationwide agencies, brand names insurance companies, etc. "Online quotes can easily help drivers obtain better car insurance deals. All they have to do is to complete an online form with accurate and real info, then compare prices", said Russell Rabichev, Marketing Director of Internet Marketing Company. CONTACT: Company Name: Internet Marketing CompanyPerson for contact Name: Gurgu CPhone Number: (818) 359-3898Email: cgurgu@internetmarketingcompany.BizWebsite: https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ SOURCE: Compare-autoinsurance.Org View source version on accesswire.Com:https://www.Accesswire.Com/595055/What-Are-The-Main-Benefits-Of-Comparing-Car-Insurance-Quotes-Online View photos
Pictures Credit
to request, modification Contact us at Here or collaboration@support.exbulletin.com



