Health
In head-to-head comparison tests, P-Tau217/Tau217 won slightly.
There are many different blood markers and tests available to help doctors diagnose Alzheimer's, but which one should you choose? Head-to-head studies would help answer this question, but few studies have directly compared blood tests on the same samples.
At last year's CTAD, Nick Ashtonpublished data from a small round robin study at the University of Gothenburg in Sweden comparing the performance of 26 different p-tau tests on 40 blood samples taken from people suspected of having Alzheimer's disease. p-tau217 came out on top (Conference News for November 2023Most of the tests were immunoassays.
The p-tau217/tau217 ratio was not shown. It has emerged that the percentage of fragments phosphorylated at this residue may be a more powerful marker than the absolute level of p-tau217. Two new direct comparison studies are currently being performed. Suzanne Schindler Washington University in St. Louis, Oscar Hanson and Noel Warmenhofen Researchers from Lund University in Sweden support the idea that %p-tau217 is a more accurate marker, although the differences between tests are often small. The study was described in a manuscript uploaded to medRxiv in early July and recently presented at AAIC in Philadelphia.
Warmenhoven and colleagues compared their mass spectrometry-based %p-tau217 and p-tau217 assays performed at the University of Washington with commercially available p-tau217 immunoassays from Lilly, Janssen, and ALZpath. They used plasma samples from 998 volunteers from the Swedish BioFinder-2 cohort, of which 375 were cognitively healthy and the rest had subjective cognitive impairment, MCI, AD, or dementia from another cause. Nearly all had undergone PET scans for neurofibrillary tangles, and 694 had undergone amyloid PET scans.
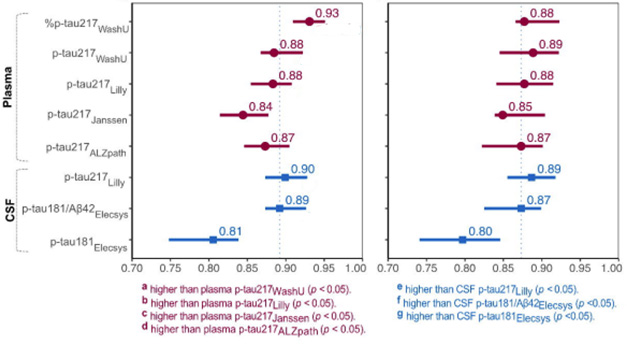
The %p-tau217 test proved to be slightly more accurate in identifying those who were amyloid positive. The p-tau217 mass spectrometry test showed similar results to the Lilly and ALZpath p-tau217 immunoassays, and all three outperformed the Janssen test. Most assays showed accuracies in the high 80s in identifying samples from Tangle-positive volunteers, with the exception of p-tau181 (image below).

Test, testPlasma tests for p-tau217 (purple) have comparable accuracy in identifying amyloid-positive (left) and tangle-positive (right) individuals in BioFinder-2. These tests are as accurate or better than CSF tests (blue), including the FDA-approved Elecsys test for p-tau181/A.b42 Manufactured by Roche (vertical dashed line for reference). [Courtesy of Warmenhoven et al., 2024.]
Additionally, the scientists compared how well each test correlated with amyloid and tangle load, as well as with the presence of both conditions, baseline cognitive scores, and decline from baseline. Across all measures, %p-tau217 correlated equally or slightly better than the other tests, with Lilly's immunoassay generally being the strongest among the immunoassays. Warmenhoven found a similar pattern in a smaller cohort of 219 volunteers from the University of Washington's Knight Alzheimer's Disease Research Center.
The authors concluded that the %p-tau217 test may be considered as the sole confirmatory test for AD, but immunoassays may be more suitable for triage. Randall BatemanCo-founder of C2N Diagnostics in St. Louis, John F. Kennedy, is a co-author on the paper. C2N sells the PrecivityAD2, a mass spectrometry-based AD test that measures %p-tau217 and the Aβ42/40 ratio.News for December 2023).
Head-to-head battle at ADNI
Meanwhile, Schindler's medRxiv manuscript reports on an analysis commissioned by the NIH Foundation Biomarker Consortium. In a previous study, the consortium compared six assays that measure plasma Aβ42/40 (Jicha et al., 2022). The current version adds the analytes %p-tau217, p-tau217, p-tau181, the glial marker GFAP, and the neurodegeneration marker NFL.
This was the largest head-to-head study to date. It compared Aβ42, Aβ40, p-tau217, tau217 from C2N, Lumipulse tests from Fujirebio Diagnostics (p-tau217 and Aβ42 and Aβ40), Quanterix p-tau217 from ALZpath, LucentAD Quanterix p-tau217 from Janssen, NeuroToolKit tests from Roche Diagnostics (p-tau181, Aβ42/Aβ40, GFAP, NfL), and Neurology 4-Plex tests from Quanterix (p-tau181, Aβ42/Aβ40, GFAP, NfL). Most of these tests are commercially available.
First author at AAIC Kellen PetersenResearchers at the University of Washington reported that the scientists performed each of these tests on aliquots of 392 samples taken from the ADNI cohort. They first evaluated each test's ability to detect people with brain amyloid. They then correlated each test with each participant's tau PET status, cortical atrophy, and cognitive impairment.
Again, %p-tau217 measured by C2N generally performed better than the immunoassay, identifying amyloid positive individuals with an accuracy of 0.87. The ALZpath and Fujirebio p-tau217 assays came in a close second with accuracies of 0.84 and 0.83 respectively, followed by Janssen at 0.82. All performed significantly better at detecting brain amyloid than the p-tau181, GFAP and NfL tests (table below).
The same pattern was seen when correlating tests with amyloid burden, and not just positivity rates defined at specific cutoffs. Including Aβ42/40 ratios where available, such as on the C2N and Fujirebio platforms, did not significantly improve performance.

P-Tau 217. AgainOf the 392 people tested in the ADNI cohort, plasma %p-tau217 most accurately identified those with brain amyloid, with p-tau217 immunoassay coming in a close second. [Courtesy of Schindler et al., 2024.]
In general, the tests performed well in the plasma of the subgroup of 192 volunteers with cognitive impairment, i.e., people who would be eligible for biomarker testing in clinical practice under current guidelines. Here, adding plasma Aβ42/40 data improved the situation slightly, with both Fujirebio and C2N tests showing 90 percent accuracy. “This means that immunoassays perform as well as mass spectrometry assays when trying to determine whether people with cognitive impairment have Alzheimer's,” says Schindler. In prevention studies, or clinical trials enrolling people without cognitive impairment, mass spectrometry tests may provide better results.
Interestingly, in people who were amyloid-negative by PET, including plasma Aβ42/40 improved accuracy the most: “The plasma Aβ42/40 ratio seems to be useful very early in the disease course, when amyloid levels are low,” says Schindler. Then, as p-tau217 starts to increase and Aβ42/40 changes plateau, the latter becomes less useful.
For other outcome measures (tau PET, cortical thickness, and dementia severity), the strongest correlation was seen for %p-tau217 and p-tau217 tests (image below). “This is noteworthy because now we have different markers for amyloid, tau, and neurodegeneration, or ATN,” Schindler said. Conference News for November 2023 “Based on diagnostic criteria. Why use Aβ42/40 or NfL when p-tau217 is better?”

One size fits all. Rather than using separate markers for “ATN” i.e. amyloid, tau and AD neurodegeneration, wouldn’t p-tau217 be sufficient? In ADNI, it correlated best with amyloid, tangles, atrophy and cognitive impairment. [Courtesy of Schindler et al., 2024.]
Goodbye lumbar puncture?
What does all this mean for CSF testing? In Schindler's view, given the superior performance of some plasma tests, it is becoming increasingly difficult to justify obtaining CSF via lumbar puncture. “The main reason clinicians still perform lumbar punctures is because blood tests aren't covered by insurance,” Schindler told Alzforum.
C2N and Fujirebio have submitted applications to the FDA, and other companies may soon follow. Given the current momentum in the AD field, some AAIC scientists are hopeful that approval for a plasma test could come as early as next year. “You're going to see blood testing in most people in the not-too-distant future,” Schindler said. Other AAIC researchers echo that sentiment. —Tom Fagan
News Quotes
- Plasma p-tau-217 testing is useful but not diagnostic
- Two new p-Tau217 blood tests join crowded field
- New Alzheimer's diagnostic criteria remain 'research only'
Citation
-
Zicha S, Bateman RJ, Shaw LM, Zetterberg H, Bannon AW, Horton WA, Baratta M, Kolb HC, Dobler I, Mordashova Y, Saad ZS, Raunig DL, Spanakis EM, Li Y, Schindler SE, Ferber K, Rubel CE, Martone RL, Weber CJ, Edelmayer RM, Meyers EA, Bollinger JG, Rosenbaugh EG, Potter WZ, Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (FNIH) Biomarker Consortium Plasma Aβ as a predictor of amyloid positivity in Alzheimer's disease Project Team..
Comparative analytical performance of multiple plasma Aβ42 and Aβ40 assays and predictive ability of positron emission tomography amyloid positivity.
Alzheimer's disease DementiaJuly 12, 2022;
Publisher.
No further information available
|
Sources 2/ https://www.alzforum.org/news/conference-coverage/head-head-testing-p-tau217tau217-comes-out-top-hair The mention sources can contact us to remove/changing this article |
What Are The Main Benefits Of Comparing Car Insurance Quotes Online
LOS ANGELES, CA / ACCESSWIRE / June 24, 2020, / Compare-autoinsurance.Org has launched a new blog post that presents the main benefits of comparing multiple car insurance quotes. For more info and free online quotes, please visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/the-advantages-of-comparing-prices-with-car-insurance-quotes-online/ The modern society has numerous technological advantages. One important advantage is the speed at which information is sent and received. With the help of the internet, the shopping habits of many persons have drastically changed. The car insurance industry hasn't remained untouched by these changes. On the internet, drivers can compare insurance prices and find out which sellers have the best offers. View photos The advantages of comparing online car insurance quotes are the following: Online quotes can be obtained from anywhere and at any time. Unlike physical insurance agencies, websites don't have a specific schedule and they are available at any time. Drivers that have busy working schedules, can compare quotes from anywhere and at any time, even at midnight. Multiple choices. Almost all insurance providers, no matter if they are well-known brands or just local insurers, have an online presence. Online quotes will allow policyholders the chance to discover multiple insurance companies and check their prices. Drivers are no longer required to get quotes from just a few known insurance companies. Also, local and regional insurers can provide lower insurance rates for the same services. Accurate insurance estimates. Online quotes can only be accurate if the customers provide accurate and real info about their car models and driving history. Lying about past driving incidents can make the price estimates to be lower, but when dealing with an insurance company lying to them is useless. Usually, insurance companies will do research about a potential customer before granting him coverage. Online quotes can be sorted easily. Although drivers are recommended to not choose a policy just based on its price, drivers can easily sort quotes by insurance price. Using brokerage websites will allow drivers to get quotes from multiple insurers, thus making the comparison faster and easier. For additional info, money-saving tips, and free car insurance quotes, visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ Compare-autoinsurance.Org is an online provider of life, home, health, and auto insurance quotes. This website is unique because it does not simply stick to one kind of insurance provider, but brings the clients the best deals from many different online insurance carriers. In this way, clients have access to offers from multiple carriers all in one place: this website. On this site, customers have access to quotes for insurance plans from various agencies, such as local or nationwide agencies, brand names insurance companies, etc. "Online quotes can easily help drivers obtain better car insurance deals. All they have to do is to complete an online form with accurate and real info, then compare prices", said Russell Rabichev, Marketing Director of Internet Marketing Company. CONTACT: Company Name: Internet Marketing CompanyPerson for contact Name: Gurgu CPhone Number: (818) 359-3898Email: cgurgu@internetmarketingcompany.BizWebsite: https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ SOURCE: Compare-autoinsurance.Org View source version on accesswire.Com:https://www.Accesswire.Com/595055/What-Are-The-Main-Benefits-Of-Comparing-Car-Insurance-Quotes-Online View photos
to request, modification Contact us at Here or collaboration@support.exbulletin.com



