Health
COVID-19 Survivor’s Serious Ongoing Symptoms
The COVID-19 pandemic infects more than 40 million people worldwide. Despite the high mortality rates seen in inpatients, little is known about the medium- to long-term effects of COVID-19 disease after discharge, but many survive. Although primarily respiratory illness, new data suggest that multiple organ dysfunction is common, especially in moderate to severe infections.New survey published on preprint server medRxiv* October 2020 describes the aftereffects of the illness in the months following recovery.
Multiple organ failure due to COVID-19
COVID-19 is primarily a respiratory or pneumoniaous disease, but due to data coming from around the world, multiple organs appear to be affected by the virus when the infection is severe or moderate. The most susceptible organs are the brain, heart, gastrointestinal system, and kidneys.
This widespread mechanism of injury is a dysregulation of the immune response mediated by the virus, which can lead to overwhelming inflammation, endothelial damage, abnormal coagulation, and consequent damage. Results depend on the degree of infection, inflammation, and individual pre-infection health.
The association between abnormal inflammation and chronic COVID-19 sequelae has been shown. Some researchers have shown that convalescent patients show lung inflammation even months after recovery. This can be another organ.

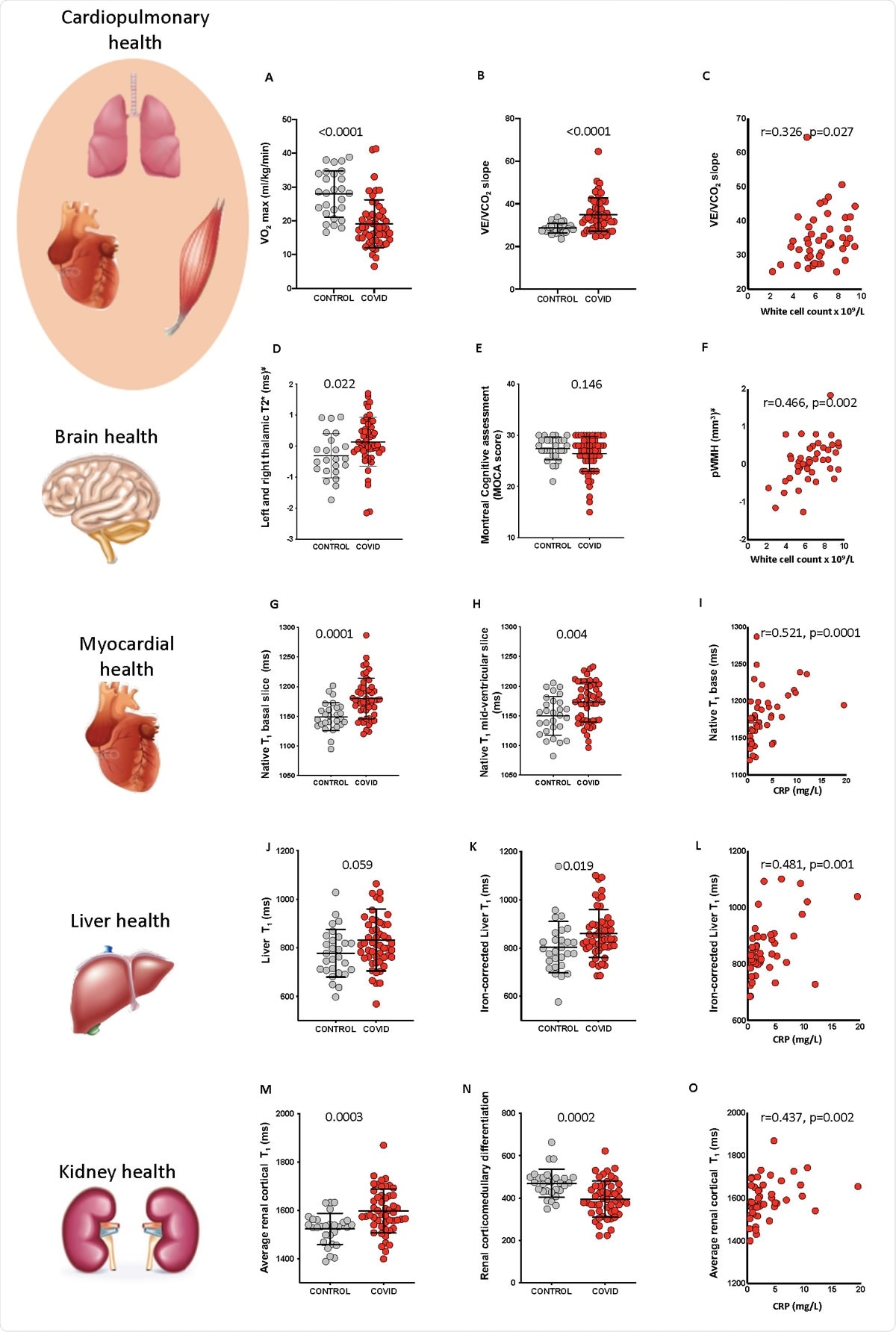
Relationship between systemic effects of COVID-19 and inflammatory response. A, B: Comparison of cardiopulmonary motility test (CPET) parameters (VO2max and VE / VCO2) between controls with consistent comorbidities and COVID-19 survivors. C: Relationship between VE / VCO2 and white blood cell count in COVID-19. D, E: Magnetic susceptibility-enhanced T2 * signal (left and right thalamus) and comparison of MoCA scores between control and COVID-19 survivors. F: Relationship between periventricular white matter hyperintensity (pWMH) and white blood cell count in COVID-19. G, H: Comparison of myocardial native T1 (basal and central chamber) between controls and COVID-19 survivors. I: Basic relationship between native T1 and C-reactive protein (CRP). J, K: Comparison of liver T1 and iron-corrected liver T1 between controls and COVID-19 survivors. These values cannot be compared to the Liver MultiScanc T1 because the iron correction T1 was calculated using an in-house algorithm. L: Relationship between iron-corrected liver T1 and CRP in COVID19. M, N: Comparison of mean cortical kidney T1 and cortical medulla differentiation in controls and COVID-19 survivors. O: Relationship between mean cortical kidney T1 and CRP for COVID-19 (comparative p-values are from Student’s t-test for all variables. Spearman correlation coefficients and p-values are reported for correlation. # Variables with p-values Gaussianized and deconfounded).
Understanding the sequelae of COVID-19
Current research aims to understand how athletic performance, intellectual functioning, mental health, and quality of life are affected by the disease. They survived moderate to severe seizures of COVID-19, were discharged 2-3 months after the onset, had persistent inflammation in multiple organs, and evaluated their effects in terms of actual health.
The study included 30 controls with the same comorbidity profile as 58 discharged COVID-19 patients. Prospective studies used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), gait tests, and other evaluation scales to look for inflammation and damage to multiple organs.
Persistent symptoms and signs of organ damage
They found that persistent shortness of breath was present in two-thirds of patients and that more than half of patients were tired. Imaging revealed lung abnormalities in 60% of patients, but heart and kidney changes in one-quarter to half, respectively. Only one-tenth showed liver damage.
Physical fitness was significantly reduced, as indicated by impaired exercise tolerance and walking distance within 6 minutes.
Other observable changes included abnormalities in different parts of the brain, but cognitive abilities were impaired in both the execution and visuospatial areas. Patients (10%) and kidneys (29%). Damage to multiple organs during convalescence correlates with inflammatory markers and the severity of acute illness and provides prognostic value for the latter.
Moderate to severe anxiety and depression have been reported in more than one-third of patients, mainly due to persistent shortness of breath when the virus test is negative. Overall, they reported a significant reduction in the quality of life they enjoyed compared to controls. Most of this disorder was due to loss of physical condition, continued shortness of breath, and fatigue, which prevented activities of daily living from proceeding normally.
Inflammation after chronic virus is key
This study has received medium-term attention to the sequelae of COVID-19 in surviving patients. The lungs and other organs are more likely to show MRI evidence of abnormalities, probably due to ongoing chronic inflammation. The finding of lung parenchymal abnormalities in many patients with MRI is consistent with previous studies revealing the presence of persistent inflammation in 71% of survivors even 3 months after discharge.
Similarly, during the months and years following the early outbreak of SARS, many survivors experienced permanent lung damage and impaired lung function. Decreased lung function in up to 13% of survivors has recently been reported by other researchers.
There is a lot of evidence that SARS-CoV-2 is overpriced Viral load And ACE2 receptors and TMPRSS2 are found at high levels in the lungs, kidneys, heart and brain. These are required for virus invasion and virus replication into host cells and indicate the virus’s tropism towards organs other than the lungs.
Despite the neurological symptoms of half of the patients in this study, MRI was unable to show severe brain damage in most cases. This may be due to microvascular injury, as indicated by the presence of calcification and the products of blood breakdown. This may explain the tendency of these images to show an increase in white matter hyperintensity and an increased incidence of stroke in these patients.
Impact and future direction
Increased blood coagulation and chronic inflammation of nerve tissue can lead to brain damage secondary to vascular damage in these patients. This may be the reason why they also experience cognitive decline in executive area, primarily reflecting impaired executive function. These findings should trigger future research on the association between cognitive impairment and COVID-19.
Up to one-third of COVID-19 patients requiring hospitalization suffer from acute myocardial injury, which predicts an increased risk of death. Cardiac MRI is useful in this situation. Previously, this modality showed that up to 60% of patients had severe inflammation of the heart tissue during convalescence and one-third of this subgroup had to be hospitalized.
In the current study, only one-quarter of patients show the presence of heart inflammation and correlate with inflammatory serum markers. This may require additional work on the comparability of different studies with different patient cohorts using different reference ranges and methods.
Liver damage in COVID-19 survivors may also be due to the effects of drugs used to treat hyperinflammation, abnormal liver metabolism due to hypoxia, venous thrombosis, and infections. Bile duct cells may also be susceptible to direct infection because the ACE2 receptor is present in these cells. More than one-tenth of convalescent patients have persistently high liver biomarkers in 2-3 months, and 10% have fibrotic inflammation markers. This correlates to some extent with MRI findings.
Kidney damage is thought to be due to long-term renal inflammation, accompanied by loss of cortical medulla differentiation. This pattern is not unique to COVID-19 and is found in other post-inflammatory damage to the glomerulus.
Researchers conclude that the chronic inflammatory response is the cause of evidence of persistent damage to multiple organs, not the outbreak of serious illness, but the immunopathology of the infection.
They are,”Further efforts to understand the role of the specific immunopathological mechanisms underlying this inflammatory process, and strategies to prevent them, limit the long-term adverse effects of COVID-19 on critical organs. May be important in.. “
About one-third of patients discontinued physiotherapy due to malaise and muscle aches. This indicates that muscle wasting can occur. It is known to be associated with severe illnesses that induce catabolic states. Therefore, this can significantly contribute to the illness effects observed during the recovery period, as well as lung damage.
More research is needed to understand how psychological damage is associated with systemic or neurological inflammation after COVID-19. However, it is clear that interdisciplinary care is needed to help survivors regain better quality of life and health after discharge.
The researchers summarize:This is the first exploratory study to comprehensively assess multiple critical organs, mental, cognitive, and physical health of post-discharge patients with COVID-19.These findings underscore the need for larger studies... “
*Important Notices
medRxiv publishes unpeer-reviewed preliminary scientific reports and should not be considered definitive, guide clinical / health-related behaviors, or be treated as established information.
..
What Are The Main Benefits Of Comparing Car Insurance Quotes Online
LOS ANGELES, CA / ACCESSWIRE / June 24, 2020, / Compare-autoinsurance.Org has launched a new blog post that presents the main benefits of comparing multiple car insurance quotes. For more info and free online quotes, please visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/the-advantages-of-comparing-prices-with-car-insurance-quotes-online/ The modern society has numerous technological advantages. One important advantage is the speed at which information is sent and received. With the help of the internet, the shopping habits of many persons have drastically changed. The car insurance industry hasn't remained untouched by these changes. On the internet, drivers can compare insurance prices and find out which sellers have the best offers. View photos The advantages of comparing online car insurance quotes are the following: Online quotes can be obtained from anywhere and at any time. Unlike physical insurance agencies, websites don't have a specific schedule and they are available at any time. Drivers that have busy working schedules, can compare quotes from anywhere and at any time, even at midnight. Multiple choices. Almost all insurance providers, no matter if they are well-known brands or just local insurers, have an online presence. Online quotes will allow policyholders the chance to discover multiple insurance companies and check their prices. Drivers are no longer required to get quotes from just a few known insurance companies. Also, local and regional insurers can provide lower insurance rates for the same services. Accurate insurance estimates. Online quotes can only be accurate if the customers provide accurate and real info about their car models and driving history. Lying about past driving incidents can make the price estimates to be lower, but when dealing with an insurance company lying to them is useless. Usually, insurance companies will do research about a potential customer before granting him coverage. Online quotes can be sorted easily. Although drivers are recommended to not choose a policy just based on its price, drivers can easily sort quotes by insurance price. Using brokerage websites will allow drivers to get quotes from multiple insurers, thus making the comparison faster and easier. For additional info, money-saving tips, and free car insurance quotes, visit https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ Compare-autoinsurance.Org is an online provider of life, home, health, and auto insurance quotes. This website is unique because it does not simply stick to one kind of insurance provider, but brings the clients the best deals from many different online insurance carriers. In this way, clients have access to offers from multiple carriers all in one place: this website. On this site, customers have access to quotes for insurance plans from various agencies, such as local or nationwide agencies, brand names insurance companies, etc. "Online quotes can easily help drivers obtain better car insurance deals. All they have to do is to complete an online form with accurate and real info, then compare prices", said Russell Rabichev, Marketing Director of Internet Marketing Company. CONTACT: Company Name: Internet Marketing CompanyPerson for contact Name: Gurgu CPhone Number: (818) 359-3898Email: cgurgu@internetmarketingcompany.BizWebsite: https://compare-autoinsurance.Org/ SOURCE: Compare-autoinsurance.Org View source version on accesswire.Com:https://www.Accesswire.Com/595055/What-Are-The-Main-Benefits-Of-Comparing-Car-Insurance-Quotes-Online View photos
Pictures Credit
to request, modification Contact us at Here or collaboration@support.exbulletin.com



